TL;DR: The KYC Due Diligence Checklist UK is essential for Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulation compliance and the prevention of financial crime. By using a KYC Due Diligence Checklist, businesses can improve customer experience and reduce fraud. Effective KYC Due Diligence ensures safe business relationships, reduced drop-offs, and full compliance.
What is KYC and Customer Due Diligence (CDD)?
Know Your Customer (KYC) is the process of confirming who a customer is and whether it is appropriate to do business with them. According to the Money Laundering, Terrorist Financing and Transfer of Funds (Information on the Payer) Regulations 2017, customer due diligence (CDD) is mandated and necessary.
It requires firms to identify beneficial owners, understand the purpose of the relationship, as well as assess for terrorist financing risk. In practice, customer due diligence solutions require checking reliable documents and data. By determining how risky a potential customer or transaction is for regulatory compliance, teams can avoid any potential money laundering.
Increasingly, this risk management is now delivered through configurable digital workflows that translate written compliance policies into consistent customer journeys. The due diligence process begins from the first sign-up all the way through to continuous monitoring.
The Three Categories of Due Diligence
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) measures are usually split into three categories to match different risk levels. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) describe a risk-based approach (RBA) as central in helping firms focus effort on higher-risk customers while keeping low-risk journeys fast and efficient.
Building and selecting different workflows based on customer’s activities is crucial to stop money laundering. By looking at the customer’s identity, account files, customer transactions, geography, and delivery channel, firms can specialize rather than relying on a one-size-fits-all process.
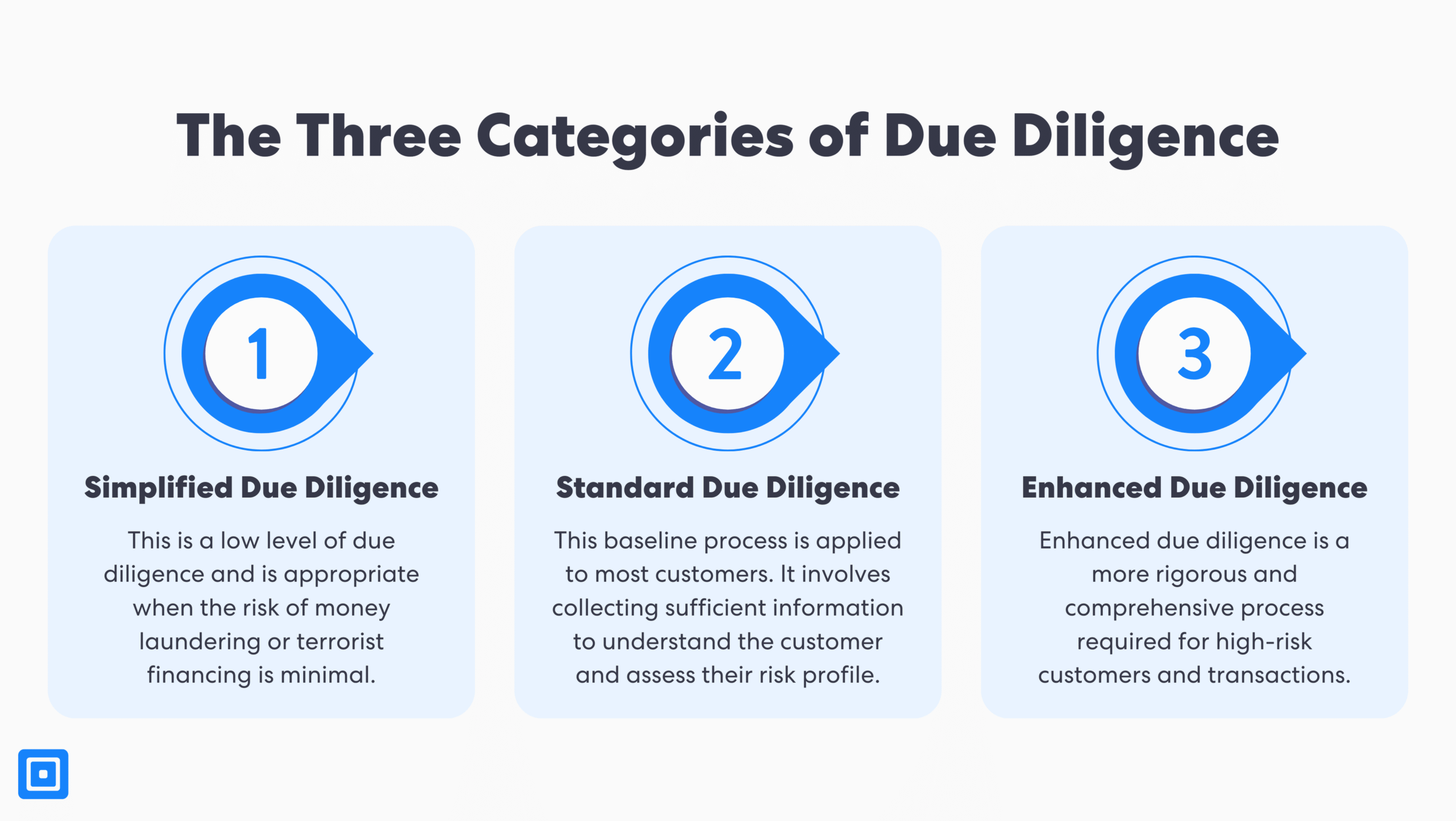
Simplified Due Diligence (SDD)
SDD is meant for low-risk customers or occasional transactions. The diligence check customers experience is far less intensive than others, but it is not optional. A well-designed SDD compliance workflow might include light-touch checks for risk management such as multi-bureau verification, sanctions screening, PEP screening, and basic document or biometric checks.
Standard Due Diligence (CDD)
On the other hand, CDD measures apply to potential customers and standard business activities or situations. A good majority of transactions fall under this type of risk mitigation. Here, a standard workflow would combine full identity verification, address verification, AML screening, and continuous monitoring rules that match the organization’s risk needs and threshold.
Enhanced Due Diligence (SDD)
Finally, EDD is only reserved for higher-risk scenarios. This type of due diligence occurs when dealing with Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs), complex ownership structures, and different jurisdictions. It involves collecting more KYC documents, source of funds verification to prevent money laundering, and conducting ongoing monitoring of business transactions. You can learn more about the intricacies here: Navigating the World of Enhanced Due Diligence.
Who Must Comply with Customer Due Diligence Measures
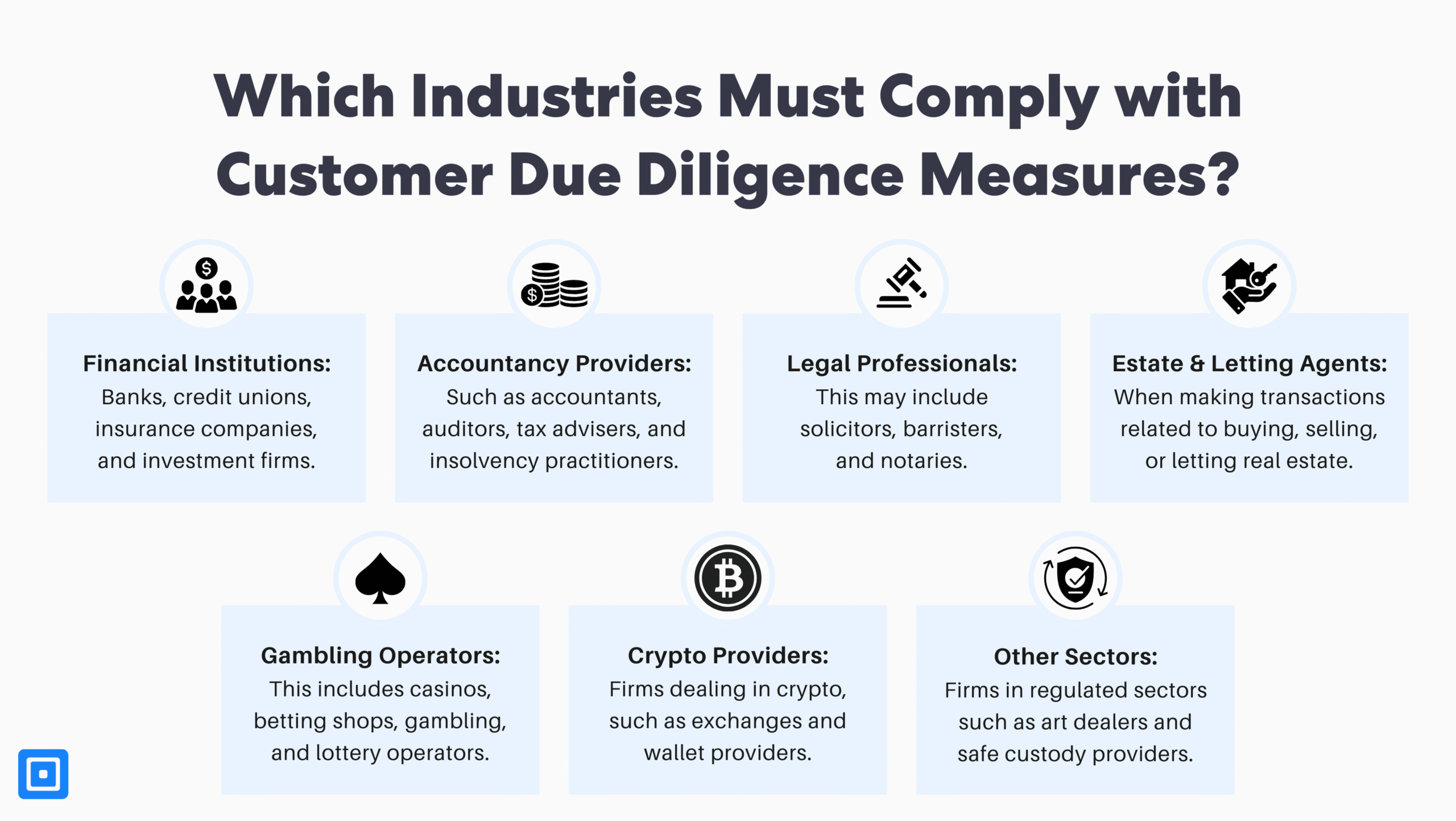
UK CDD measures apply to a broad set of regulated businesses within the financial sector. This includes banks, accountancy providers, legal professionals, estate agents, crypto providers and so much more.
For all of these sectors, compliance workflows are essential to avoid money laundering risks. Each industry will have different customer types, onboarding channels, and products. Therefore, every sector has specific legal obligations requiring different policy-driven workflows that apply SDD, CDD, and EDD proportionately based on risk.
When is KYC Due Diligence Checklist UK Required?
Financial institutions and other regulated businesses must apply customer due diligence (CDD) measures at specific trigger points. In order to stay compliant and prevent financial crime, money laundering, and terrorist financing, firms must use a checklist during these scenarios::
- When establishing a new business relationship: Verify the customer’s identity and risk profile before providing services, using a KYC workflow aligned to their segment and risk level.
- For large or unusual one-off financial transactions: Run CDD (or EDD) when a transaction exceeds set thresholds, even if there is no existing relationship, with workflow rules automatically flagging these cases.
- When suspicious activity is detected for potential customers: Apply EDD and escalate through case management workflows whenever there are signs of financial crime or unexplained behaviour.
- When existing customer data is unreliable or outdated: Re-verify identity and refresh CDD if there are doubts about the accuracy or completeness of previous information.
- When ownership or business circumstances change: Reassess risk and update verification when there are material changes in beneficial ownership, activities, or risk profile.
By designing no-code workflows for these example scenarios with such triggers, firms can protect their financial system, support AML efforts, and reduce reliance on ad hoc manual decisions.
The Five Key Components of a KYC Due Diligence UK Checklist
Now, before choosing individual checks, organizations should map their CDD process policy into clear workflows that can be tailored to varying customer risk profiles and jurisdictions. Embedding these flows as configurable, automated steps keeps scrutiny, approvals, and audit trails aligned with compliance policies. Strong due diligence in the UK usually includes five core components:
1. Customer Identification and Verification
The initial step in the KYC Due Diligence process is verifying customer identities. Firms and other financial institutions rely on official documents such as passports, driving licences, bank statements, or utility bills. They also increasingly use biometrics to confirm the genuine identity of the owner. Customer due diligence requirements specify acceptable documents, verification methods, and when additional checks or manual review are required.
In workflow terms, firms define separate flows for individual customers and legal entities by embedding these steps into reusable onboarding templates. This act ensures every new potential customer is asked for the right information at the right time, regardless of channel or product.
2. Beneficial Ownership Identification
If the customer is a company, partnership, or acting on behalf of someone else, then identifying the Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO) is mandatory. According to gov.UK, the UBO is the natural person who ultimately owns or controls the entity, even where ownership chains span across multiple jurisdictions or nominee arrangements.
A good checklist can set out what ownership information must be collected, which sources should be consulted, and when a structure is considered incredibly complex or high risk. From this, workflows can flag higher-risk cases for Enhanced Due Diligence redirection to route them into specialist review queues with additional checks and approvals.
3. Understanding the Purpose and Intended Nature of the Business Relationship
Another important part of customer due diligence is understanding why they want to form a business relationship or carry out a transaction. Firms can learn this information by asking about source of funds, expected transaction volumes, main counterparties, and how the product will be used.
By building conditional questionnaires into the onboarding journey and feeding responses into a risk-scoring engine, teams can select an appropriate due diligence workflow and monitoring intensity. Any context can also help investigators later when they review alerts and assess whether a transaction genuinely looks suspicious.
4. Adopting a Risk-Based Approach (RBA)
Often, RBA helps firms decide how much due diligence to apply to each customer and transaction. Risk factors can consider geography, sector, transaction size and frequency, delivery channel, customer type, and adverse media history. Higher-risk customers will usually require EDD, while genuinely low-risk customers may qualify for SDD.
To manage this at scale, firms codify risk criteria into policy and use automation rules to translate risk scores into specific workflow templates. This allows programs to be proportionate and consistent, while still allowing compliance teams to adjust thresholds centrally as regulation or risk appetite evolves.
5. Ongoing Monitoring and Record Keeping
Due diligence does not end at onboarding. It is critical to monitor transactions and behavior throughout the entire customer journey to ensure activities remain consistent with the stated purpose and risk profile. This is essential in detecting suspicious patterns early. They also need detailed records of checks, decisions, and evidence used.
Therefore, a checklist must include rules for ongoing monitoring, re-screening schedules for sanctions and PEP lists, and triggers for refreshing historical information. Embedding these policy rules into workflows and case management provides a clear, reportable audit trail while keeping manual effort under control.
Case Study: Danske Bank Missed Links to Terrorist Financing via Shell Companies
Problem
Between 2007 and 2015, Danske Bank’s Estonian branch processed more than €200 billion in suspicious transactions through shell companies with opaque ownership. Weak onboarding, failure to verify UBOs properly, and inadequate transaction monitoring meant links to criminal and terrorist networks went undetected, leading to severe regulatory and reputational fallout.
Solution
Following further investigation, Danske Bank shut down non-domestic operations at the branch, overhauled its full AML framework, and embedded stricter CDD and EDD into automated workflows. This included mandatory UBO verification, improved source-of-funds checks, risk-based financial transaction monitoring, and tighter screening against sanctions/PEP and adverse media lists.
Outcome- Terminated thousands of high-risk customer accounts with due diligence customer processes
- Rebuilt onboarding journeys for legal entities with stricter KYC and UBO checks
- Introduced ongoing audits, stronger governance, and enhanced board oversight
- Sharply increased focus on risk-based monitoring and regulatory expectations
- Incurred significant financial and reputational costs, underscoring the price of CDD failures
Tailoring Journeys to Risk and Customer Experience
Designing a customer due diligence process from a compliance perspective is no longer enough. Firms must blend policy, automation, and customer experience into a single onboarding and monitoring strategy that is both regulator-ready and user-friendly. Low-risk users must move quickly through lighter-touch SDD workflows, while higher-risk profiles go through longer, detailed journeys.
Analytics on completion rates and drop-off points help teams continually refine these workflow journeys. Light-touch SDD flows that combine multi-bureau checks, AML screening, and document and biometric verification into a single guided experience can dramatically reduce friction for customers and abandonment without weakening AML defences.
The Importance of Investing in Staff Training and Awareness
The top tips and solutions above can help businesses implement and improve their Customer Due Diligence (CDD) measures. However, one crucial aspect that is always forgotten about in compliance strategies is staff training and compliance. Comprehensive training on AML and KYC will empower compliance teams to stay informed on the latest legislation updates and regulation technology. Ultimately, risk management teams are the first line of defence in identifying suspicious activity, conducting thorough diligence checks, and maintaining strong compliance.
Common Challenges With Basic Customer Due Diligence
Despite their best efforts, many organizations struggle to turn CDD policy into practical steps to prevent money laundering. Common pain points include poor data capture, difficulty adapting to changing risk profiles, uneven application of SDD, CDD, and EDD, and fragmented tech stacks that make it hard to obtain a reliable view of the customer profile.
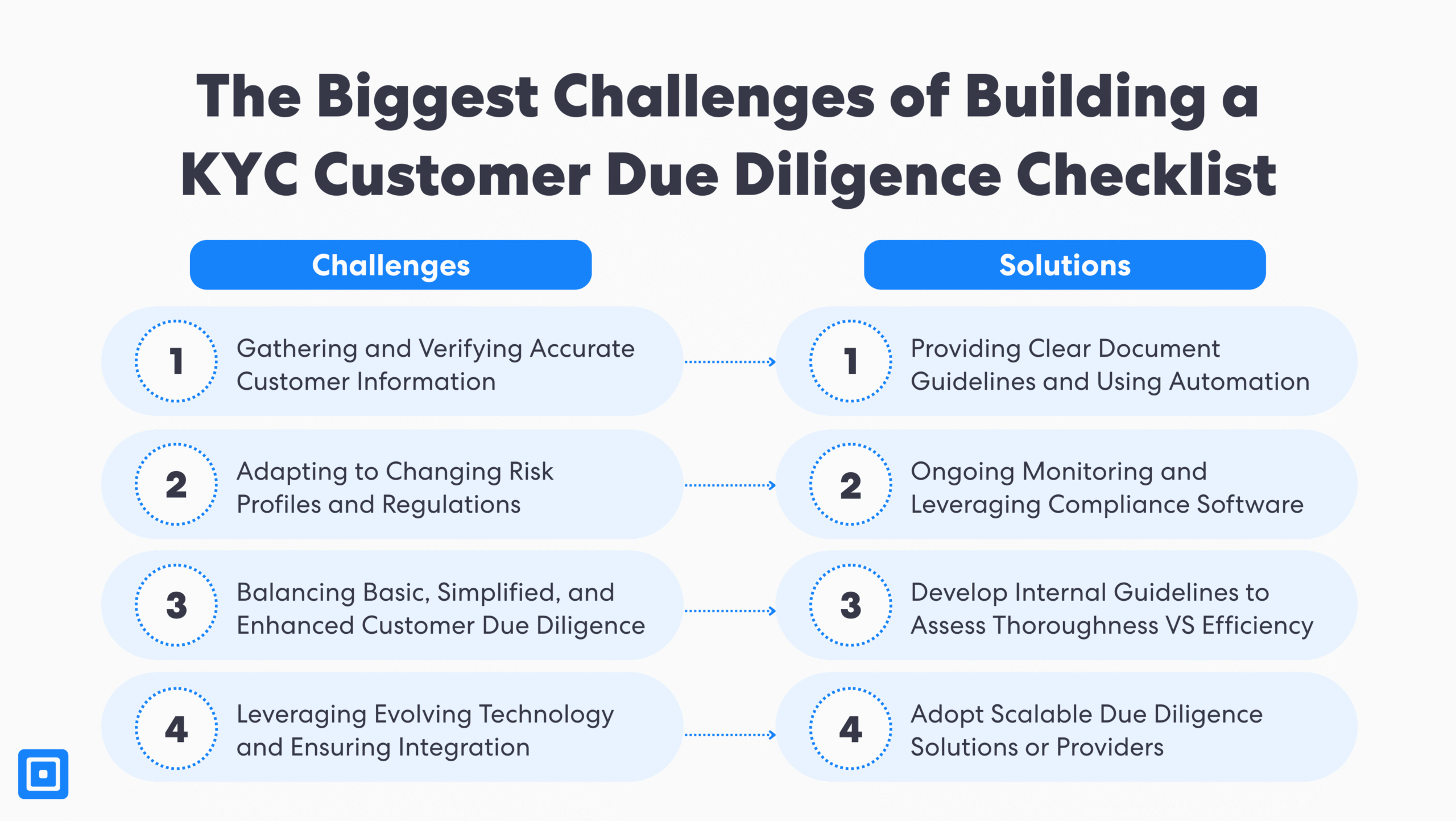
Challenge 1: Gathering and Verifying Accurate Customer Information
Collecting reliable documents to verify identity, address, and business activities is essential. However, unclear requirements (residential address versus commercial address, home phone number versus business, etc..) and clunky capture flows often lead to incomplete information as well as high drop-off rates. By standardizing document requirements, giving clear in-flow guidance, and using intuitive capture interfaces, teams can reduce rework, speeds onboarding, and improves data quality.
Challenge 2: Adapting to Changing Risk Profiles and Regulatory Requirements
Often, customer risk profiles evolve as they enter new markets, change ownership, or appear in adverse media, while regulations and high-risk lists also simultaneously shift. Effective ongoing monitoring and policy-based workflows recalculate risk scores, trigger refreshed CDD or EDD when thresholds are crossed, and roll out new policy changes across all journeys without constant manual reconfiguration.
Challenge 3: Balancing Basic, Simplified, and Enhanced Customer Due Diligence
Without a shared playbook, some teams over-apply EDD and create unnecessary friction, while others under-apply controls and expose the firm to regulatory or financial risk. Codifying thresholds and decision rules into clear guidelines and configurable workflow templates ensures SDD, CDD, and EDD are applied consistently, while still allowing central adjustments as risk assessment goals and appetite evolves.
Challenge 4: Leveraging Evolving Technology and Ensuring Integration
Many firms rely on legacy systems, spreadsheets, and disconnected tools that create data silos and slow investigations. Adopting API-first integrated KYC solutions that combine verification, screening, case management, and analytics in a single workflow engine provides a unified customer view and makes it easier to improve onboarding journeys.
Key Takeaways
- A well-structured KYC Due Diligence Checklist UK is essential to meet UK and global standards.
- Use a risk‑based approach to decide between Simplified, Standard, or Enhanced Due Diligence.
- Automate verification, screening, and workflows while preserving risk assessment policy controls.
- Tailor onboarding journeys to customer risk profiles to reduce friction and customer drop‑offs.
- Maintain ongoing monitoring, reviews, and record‑keeping to stay compliant and audit-ready.
Bolster Compliance with Robust KYC Due Diligence Checklist
Crafting a strong KYC and CDD process is critical for aligning with regulatory requirements, cost savings, as well as safeguarding customer and business relationships from financial criminals. By verifying customer identities, assessing risk accurately, and mapping policies into practical workflows, firms can tailor Simplified, Standard, and Enhanced Due Diligence to each customer segment and prove that measures are applied consistently in practice.
A dynamic, workflow-driven approach prevents financial crime, supports secure onboarding, and creates positive customer experiences while reducing remediation costs and enabling scalable compliance. To strengthen your KYC/AML process, get in touch with our team at ComplyCube to design automated workflows with deep document and biometric coverage and flexible policy controls tailored to your risk appetite.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is included in a KYC Due Diligence Checklist UK?
A UK-specific KYC Checklist includes identity verification using acceptable UK documents, beneficial ownership checks for UK-registered entities. It includes risk assessment of business relationships and customer risk profiles under UK AML regulations, and ongoing monitoring in line with guidance from HMRC, FATF and the FCA to prevent money laundering and other financial crime.
Which UK businesses are legally required to conduct customer due diligence?
Under the UK Money Laundering Regulations 2017, all regulated businesses including banks, estate agents, accountants, law firms, and cryptoasset providers operating in the UK must apply Customer Due Diligence measures when onboarding clients or processing qualifying transactions.
When must enhanced due diligence (EDD) be carried out in the UK?
UK firms must apply EDD when dealing with Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs), individuals in high-risk third countries, or any customer activities flagged as suspicious. This also includes situations where source of funds or ownership structures cannot be easily verified using UK or international registries.
How can UK-based companies automate KYC Due Diligence while complying with UK regulations?
UK-regulated firms can automate KYC by using platforms that support biometric identity verification, UK-specific document recognition, multi-bureau AML screening, and integration with UK regulatory requirements such as those enforced by the FCA, HMRC, and the NCA.
Why do UK compliance teams trust ComplyCube?
ComplyCube offers a UK-ready compliance solution with support for FCA-regulated workflows, local document coverage, multi-bureau AML screening, biometric verification, and no-code onboarding templates. Trusted by UK financial institutions and professional services firms, ComplyCube helps ensure full compliance with UK KYC and AML standards.