The online world has revolutionized how we communicate, access information, and conduct business. Almost everything we do, from opening a new bank account to scheduling a doctor’s appointment, can be done online in just a few steps.
Nevertheless, this new reality brings about new challenges. Fraudsters are becoming increasingly sophisticated, and businesses must keep up to protect their customers, assets, and reputation while complying with increased regulatory scrutiny.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is a key Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) process. This article highlights EDD’s key aspects and challenges.
What is Customer Due Diligence?
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is a process undertaken by businesses, particularly financial institutions and regulated entities, to verify the identity of customers and assess risks before establishing a business relationship. CDD aims to prevent money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illegal activities.
A crucial element of CDD is the Know Your Customer (KYC) process, which involves verifying customer details such as name, address, date of birth, transaction history, biometrics, and identification documents.
After identity verification, businesses must conduct Ongoing Due Diligence (ODD) by continuously monitoring the customer’s risk profile and reporting suspicious activities to the competent authorities.
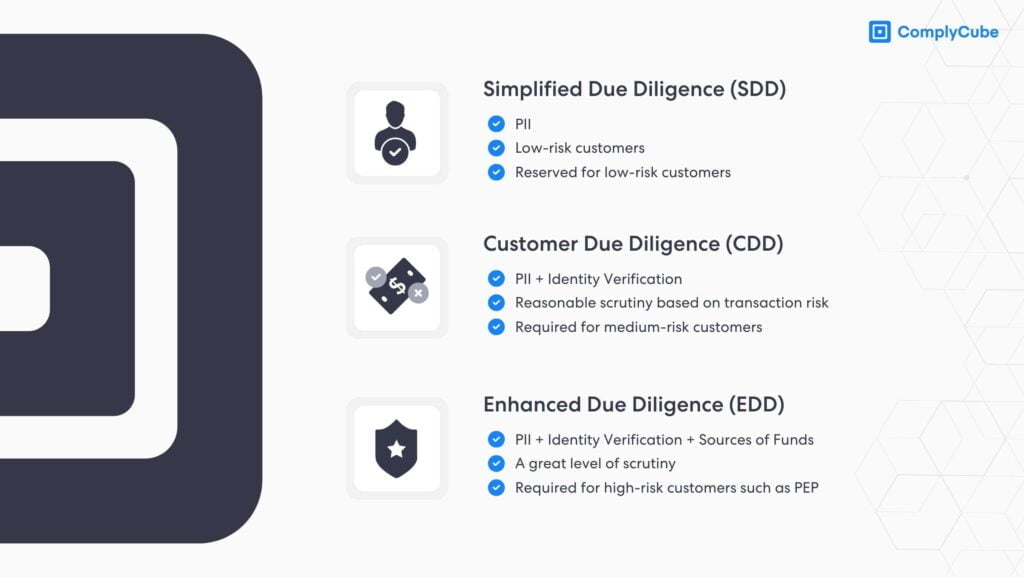
The Different Levels of CDD
There are three levels of CDD:
- Simplified Due Diligence (SDD): Applied to low-risk customers, SDD involves minimal identity verification and risk assessment. It is used when the risk of Financial Crime (FinCrime) is deemed low.
- Basic Due Diligence (BDD): Applied to most customers, BDD, also called CDD, involves obtaining and verifying customer information, including occupation, source of funds, and the purpose of the business relationship.
- Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD): Applied to high-risk customers, such as a Politically Exposed Person (PEP) or client from a jurisdiction with weak AML/CTF controls. EDD involves a deeper analysis of customer information and a thorough risk assessment.
To determine the appropriate level of CDD, businesses use a Risk-Based Approach (RBA) to assess customer risk factors such as location, the nature of transactions, and behavior. RBA enables institutions to allocate resources to higher-risk areas, enhancing the effectiveness of AML/CTF measures.
What is Enhanced Due Diligence?
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) represents a comprehensive approach to customer due diligence employed by businesses to address heightened transaction risk associated with high-risk customers.
EDD processes involve thoroughly examining client backgrounds, financial assets, sources of funds, business certificates, and transaction patterns. By obtaining additional identifying information and delving deeper into risk factors, EDD enables improved risk management compared to standard KYC diligence measures.
That is why several jurisdictions have introduced regulations requiring institutions to implement comprehensive EDD controls. Key examples include the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) in the United States and the European Union’s 6th Anti-Money Laundering Directive (6AMLD).
The Difference between AML Due Diligence and EDD
AML Due Diligence is a broad term encompassing various processes and measures financial institutions and businesses take to detect, prevent and report money laundering and other illicit activities. It includes implementing policies, procedures, and controls for identifying and assessing customer risk, as well as conducting CDD and transaction monitoring.
On the other hand, EDD is a specialized form of CDD used in situations with a higher risk of money laundering, terrorist financing, or other financial crimes. It requires a more thorough examination of a customer’s background, source of wealth, and transaction activity.
In summary, AML Due Diligence is a broad term that includes policies, procedures, and controls for assessing customer risk. EDD is a specialized and extensive process for customer vetting used in high-risk situations to gain a deeper understanding of a customer’s financial activities and identify potential risks.
When is EDD Required? Defining High-risk Customers
EDD may be triggered for customers or ongoing transactions that are considered higher risk by a financial institution. Examples include:
- Customers from high-risk countries or jurisdictions with weak AML/CTF regulations or a greater risk of money laundering. These are also known as high-risk third countries.
- Politically Exposed Persons, their family members, or close associates.
- Customers with a history of criminal activity, involvement in suspicious transactions, or high-risk businesses such as cash-intensive businesses.
- High-net-worth individuals with complex business structures or financial arrangements.
- Transactions involving high-risk industries include arms trade, gambling, the financial sector, and cryptocurrency.
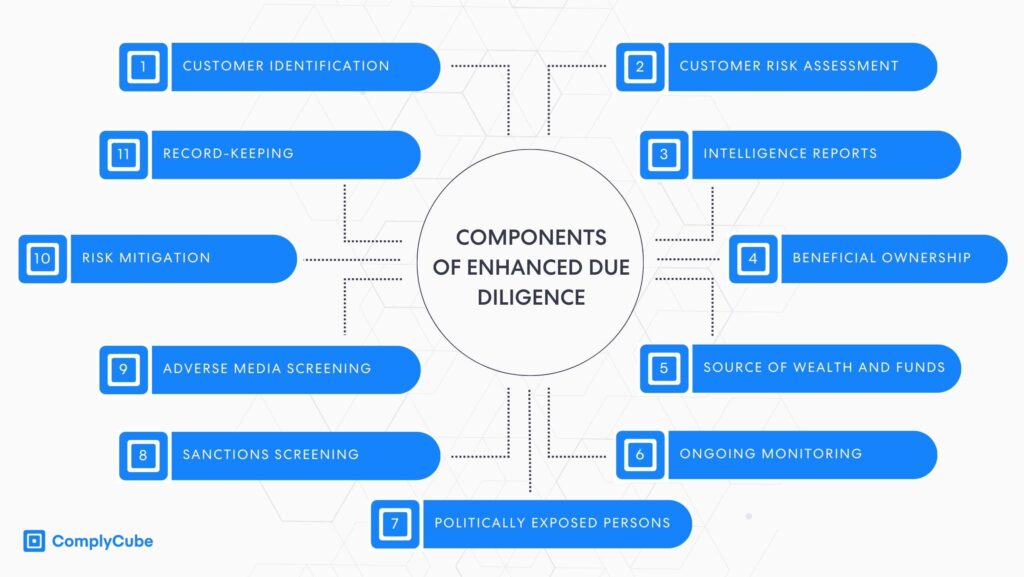
The Key Components of Enhanced Due Diligence
Enhanced due diligence procedures rely on the organization’s risk appetite but typically include the following components:
- Customer Identification Program (CIP): Verifying the customer’s identity by collecting necessary identification documents and corroborating the provided information.
- Customer Risk Assessment: Evaluating the risk level of the customer based on factors such as industry, location, transactional behavior, and affiliations.
- Intelligence Reports: Commissioning an intelligence report to obtain insights into an individual, beneficial owner, business, or industry to assess risks holistically.
- Beneficial Ownership: Identifying the ultimate beneficial owners of the customer’s business or account, including individuals who own or control the legal entity.
- Source of Wealth and Funds: Investigating discrepancies in the customer’s source of wealth, the origin of funds, and net worth.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuously monitor high-risk customer accounts to detect suspicious activity, changes in risk profile, or compliance issues.
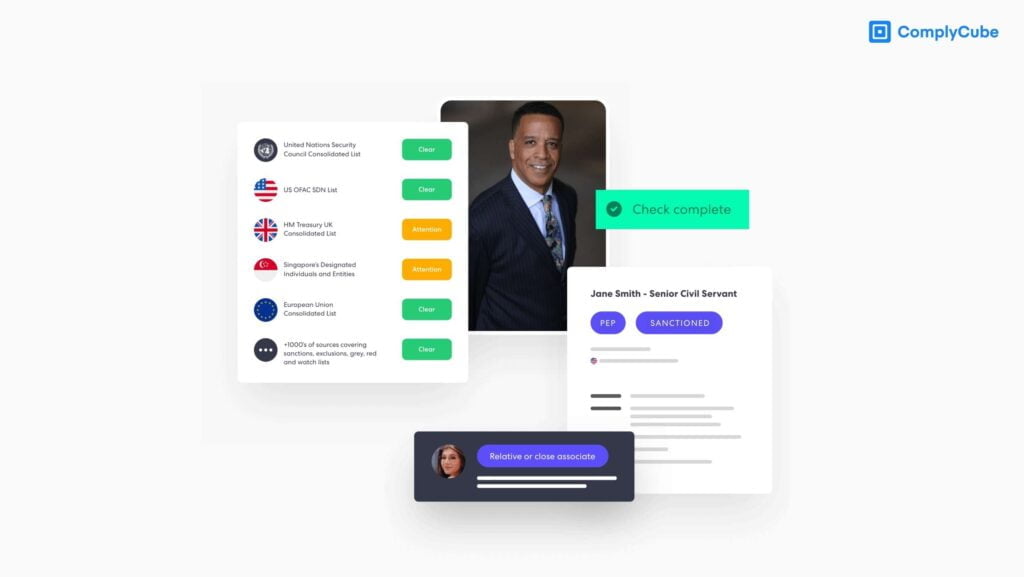
- Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs): Identifying whether the customer or a beneficial owner is a politically exposed person or has close ties with one. You can learn more about it here: What is a Politically Exposed Person (PEP)?
- Sanctions Screening: Checking the customer against national or international sanctions lists, which may prohibit or restrict business relationships. You can learn more about the topic here: What is Sanctions Screening?
- Adverse Media Screening: Reviewing news articles and online sources to identify potential involvement in FinCrime or illicit activities.
- Risk Mitigation: Implementing appropriate risk mitigation measures, such as enhanced transaction monitoring, additional documentation requirements, or senior approvals.
- Record-Keeping: Maintaining detailed records of the EDD process, including customer information, risk assessments, and any related actions.
Incorporating KYC in Enhanced Due Diligence Procedures
Incorporating KYC into EDD procedures strengthens risk management for institutions dealing with high-risk customers. The KYC process lays the groundwork for EDD by gathering essential customer information and assessing risks. When combined, these approaches create a robust customer risk management strategy.
KYC and EDD procedures involve customer identification, verification, risk assessment, and ongoing monitoring. However, EDD requires a more in-depth analysis, emphasizing beneficial ownership, extensive evaluation of the customer’s source of wealth and funds, and enhanced ongoing monitoring. This heightened level of examination enables banks and other financial institutions to gain a deeper understanding of high-risk customers and maintain regulatory compliance.
Enhanced Due Diligence Checklist
The EDD process includes several steps that can vary depending on the organization’s policies and procedures. A typical due diligence checklist might involve:
- Identifying high-risk customers and transactions that require EDD based on risk assessment criteria and thresholds.
- Obtaining additional information and documents to verify the customer’s identity, funds, and wealth involved in the transaction to assess the risk posed by the business relationship.
- Conducting a thorough analysis of the client’s financial activities, business-related documents, and transaction history.
- Investigating red flags or suspicious activity, such as payments from unknown third parties and their intended nature, and escalating to the appropriate internal or external authorities.
- Documenting findings and rich audit trails, from the client risk assessment stages and throughout the customer relationship, for future reference and compliance.
- Implementing an effective ongoing monitoring strategy for high-risk customers and transactions to ensure risk profiles remain accurate and up-to-date.

Benefits of Enhanced Due Diligence
The Enhanced Due Diligence process enables organizations to manage high-risk customers and transactions, reduce the likelihood of financial losses, legal penalties, and reputational damage, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Benefits of implementing EDD include:
- Improved Risk Management: EDD enables organizations to identify transactions from high-risk clients more effectively, which helps reduce financial and reputational risks.
- Enhanced Compliance: EDD ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, reducing the likelihood of legal penalties and regulatory sanctions.
- Better Decision Making: EDD provides in-depth insights into potential risk factors, enabling organizations to adopt a fledged risk-based approach.
- Stronger Customer Relationships: Implementing EDD demonstrates a commitment to compliance, which helps build stronger customer relationships and avoid actors that present increased exposure to money laundering risk.
- Increased Efficiency: EDD simplifies the onboarding and ongoing monitoring process, enabling organizations to address potential issues proactively.
- Competitive Advantage: By streamlining compliance, organizations can differentiate themselves from competitors and attract new business.

Challenges of Enhanced Due Diligence
As outlined earlier, enhanced due diligence measures are widely used in various industries to identify potential risks. However, implementing EDD poses challenges for businesses.
In this section, we’ll discuss some of these challenges and how to address them.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is one of the major challenges in EDD due to the complexity and diversity of the regulations that govern financial institutions. Important aspects to consider include:
- Variation in Regulations: Different jurisdictions have different rules regarding EDD. For example, what is considered adequate in one country may be deemed insufficient in another. This variance can make it challenging for institutions operating across borders to maintain consistent and compliant EDD procedures.
- Regulation Changes: Regulations are not static; they can change over time, often in response to emerging trends in FinCrime or major incidents. Institutions must stay up-to-date with these changes and quickly adapt their EDD procedures accordingly. This requires continuous monitoring of regulatory updates and changes, which can be quite challenging and resource-intensive.
- Interpretation of Regulations: Sometimes, the regulations may be open to interpretation, or they may lack clarity on specific points. This can lead to inconsistencies in how EDD is performed and can increase the risk of non-compliance.
Addressing regulatory compliance in EDD is critical for financial institutions, and it requires an integrated approach that combines staying abreast of regulatory changes, standardizing processes, leveraging Regulatory Technology (RegTech), and investing in regular staff training.
Efficiency and Effectiveness
Another key challenge in implementing EDD measures is balancing the requirement for efficiency with the need to conduct comprehensive risk assessments. Organizations must find ways to optimize processes, prevent money laundering, and maintain a great customer experience.
Organizations should invest in technology and automation tools, such as ComplyCube, which leverages Artificial Intelligence (AI), to improve the accuracy and consistency of customer risk profiles and thus improve the compliance posture.
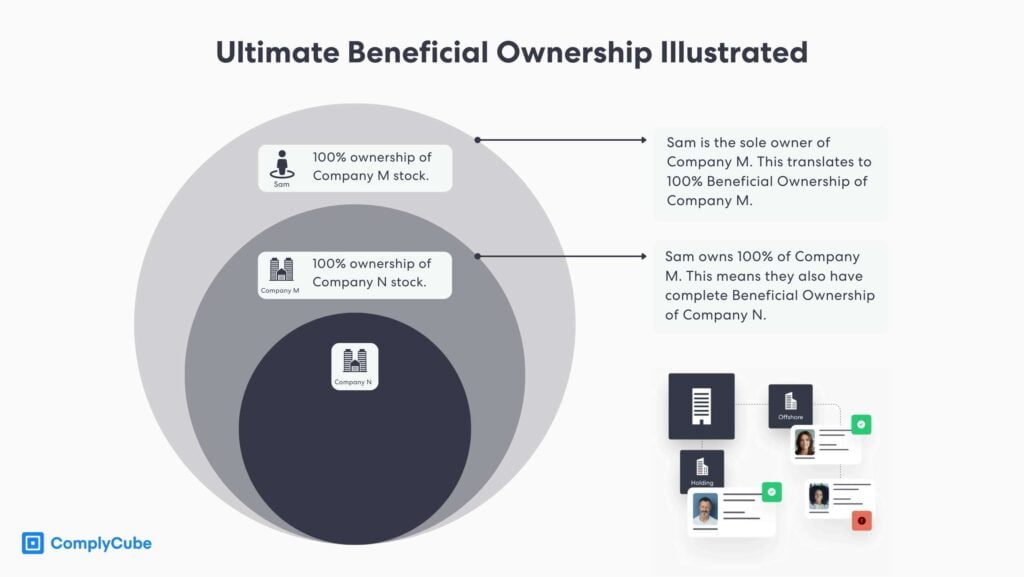
Ultimate Beneficial Ownership (UBO)
Ultimate Beneficial Ownership (UBO) poses a significant challenge for EDD due to the complexities and opacity of modern corporate structures. The prevalence of shell companies, offshore accounts, partnership agreements, and complex ownership arrangements makes determining the real owners behind legal entities labor-intensive and time-consuming.
Moreover, effective EDD requires a skilled workforce with extensive knowledge of regulatory requirements, industry-specific risks, and technological advancements. The training and development of such professionals can be expensive and time-consuming, especially for small businesses.
Virtual addresses can be also problematic for identifying UBOs and assessing financial crime risk. Institutions can conduct an on-site visit to provided address, use an electronic data verification service, and implement EDD controls that include an on-site visit to the physical address.
While regulators have made significant progress in strengthening AML/CTF measures, increased international cooperation, data-sharing initiatives, and the use of innovative technology solutions are needed to unmask hidden beneficial owners.
Adverse Media Screening
Verifiable adverse media searches are an essential component of EDD procedures. Robust adverse media screening uncovers negative information from credible sources, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and improve risk management.
Performing searches manually is inefficient, time-consuming, and susceptible to human error and biases, potentially compromising the quality and reliability of the results. It is also not cost-effective or scalable for high-volume businesses.
Automated tools using artificial intelligence and machine learning can quickly and accurately analyze vast data volumes, streamlining EDD processes and reducing human error, in line with The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations. You can find more about it here: The importance of Adverse Media checks for an effective KYC.
Data Privacy and Protection
One challenge in the EDD process is ensuring the privacy and protection of customer data, as it involves collecting and storing sensitive personal and financial information. Businesses must implement robust data security standards to safeguard customer information and prevent unauthorized access or breaches.
Ensuring that data is accurate and up-to-date is another challenging aspect of EDD from a data privacy and protection standpoint. To address this, businesses must establish procedures for maintaining accurate and relevant customer data through the use of a Single Customer View (SCV) solution.
Adherence to data protection regulations, such as GDPR, is crucial for maintaining compliance and demonstrating a commitment to responsible data management. This approach helps build trust with stakeholders, ultimately fostering a secure environment for conducting business.
Risk-based Approach
Implementing a risk-based approach within EDD is advocated by FATF. However, as bad actors continuously devise new tactics to bypass existing AML/CTF controls, staying informed of the changing risk landscape and adjusting the risk-based approach is demanding.
Organizations should establish clear risk assessment criteria and thresholds, considering indicators such as customer type, activity, geographic location, and delivery channel risk factors. Thorough assessments allow organizations to understand transaction risks, focus efforts, and proactively implement new AML controls to stay ahead of bad actors.
A risk-based monitoring strategy is crucial for regularly reviewing and updating criteria to ensure relevance and effectiveness. You can learn about it here: What is a Risk-Based Approach (RBA)?
Conclusion
As the regulatory landscape evolves, EDD remains critical to an organization’s AML/CTF processes. To mitigate emerging money laundering risks, businesses should invest in technology and automation, adopt a risk-based monitoring strategy, and prioritize data privacy and protection.
The future of EDD lies in improved information sharing among key stakeholders, such as regulators, financial institutions, private banking institutions, and law enforcement agencies. This collaborative approach will lead to standardized EDD best practices and a safer global financial system.
Looking for a global compliance platform for AML and KYC checks? Get in touch with us today!