TL;DR: What is KYC verification? It is the process businesses use to verify customer identities, assess financial crime risks, and comply with regulatory obligations. KYC verification plays a crucial role in Anti-Money Laundering (AML) efforts by preventing fraud, terrorism financing and other illicit activities.
What is KYC Verification?
KYC verification, short for Know Your Customer verification, is the process through which businesses verify the identity of their customers. It involves collecting and validating identity documents, conducting background checks and continuously monitoring customer activity. Originally developed to prevent money laundering and fraud, KYC has become a core requirement across many high-risk sectors. Businesses can build trust, meet legal obligations and protect the integrity of the financial ecosystem.
The Legislation Frameworks Governing KYC
Implementing KYC combats financial crime and terrorist financing. It is also a legal requirement across many jurisdictions. For instance, the EU’s anti-money laundering directives (AMLD), the US Patriot Act, and the guidelines of the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) mandate that businesses enforce comprehensive and auditable KYC processes. These laws drive organizations to collect, verify, and continuously monitor customer information to identify and mitigate potential risks.
The Evolution of KYC Regulations
As an essential component of broader anti-money laundering efforts, KYC has been reinforced by decades of legislation. Since the 1970s, governments have introduced laws to combat money laundering and fraudulent activities within their borders.
In 2023 alone, global regulators issued $5.8 billion in fines for AML and KYC non-compliance. This underscores the critical importance of robust KYC processes for organizations everywhere.
Here are some of the most popular AML regulations in different countries that protect financial institutions and customers worldwide.
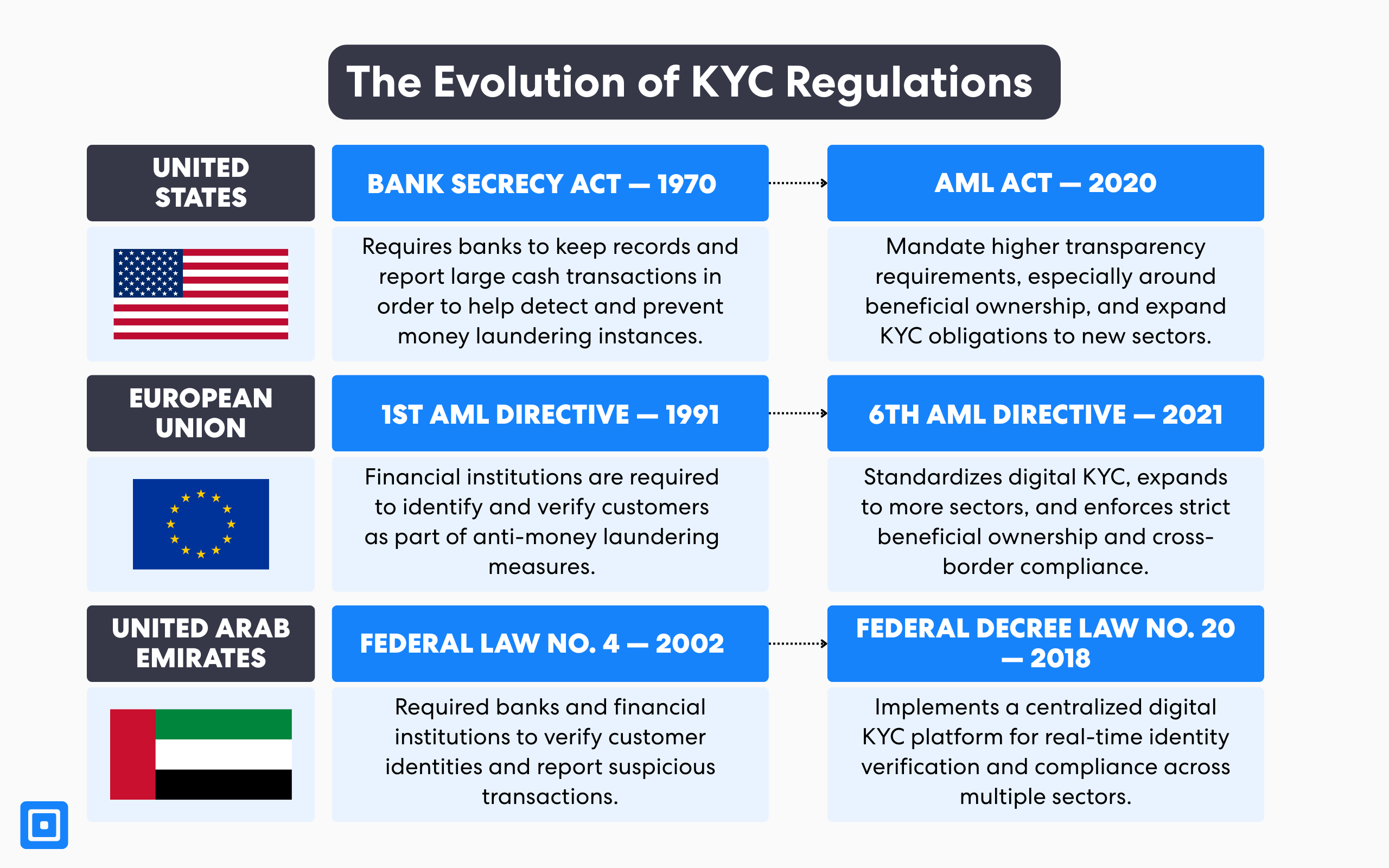
United States and The Bank Secrecy Act
In 1970 in the United States, the first regulation began with the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), which focused on recordkeeping and the reporting of large currency transactions. As technology progressed, it prompted further development of KYC regulations. This led to the US Patriot Act (2001), which expanded KYC requirements, and the adoption of the Anti-Money Laundering Act (AMLA) in 2020, which now encompasses a broader analysis of innovative technologies and their impacts on Anti-money Laundering (AML) legislation. Additionally, organizations such as the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) were established to supervise broker-dealers and ensure compliance with KYC requirements.
European Union and the First Anti-Money Laundering Directive
The first anti-money laundering directive (1AMLD) was established in the EU in 1991. Since then, it has evolved to the sixth directive (6AMLD) in 2020, aiming to close additional money laundering loopholes through stronger identity verification solutions. Key changes include enhanced cooperation among EU member states, a requirement for all to criminalize specific serious offenses, and increased penalties for individuals and entities involved in money laundering. This includes mandatory minimum prison sentences of four years.
United Arab Emirates and Federal Law No. 4 of 2002
Similarly, the UAE established clear obligations for financial institutions and other regulated entities to identify and prevent suspicious transactions. By mandating robust customer due diligence, ongoing monitoring, and KYC procedures. Its first fight against money laundering began with the enactment of Federal Law No. 4 of 2002. The framework was further strengthened by subsequent amendments, such as Federal Law No. 9 of 2014. It was ultimately replaced by Federal Decree Law No. 20 of 2018, which expanded the KYC requirements’ scope to include combating terrorist financing and financing illegal organizations.

Breaking Down the KYC Verification Process Step-by-Step
The KYC process unfolds in three main stages: Customer Identification Program (CIP), Customer Due Diligence (CDD), and lastly, the Ongoing Monitoring stage.
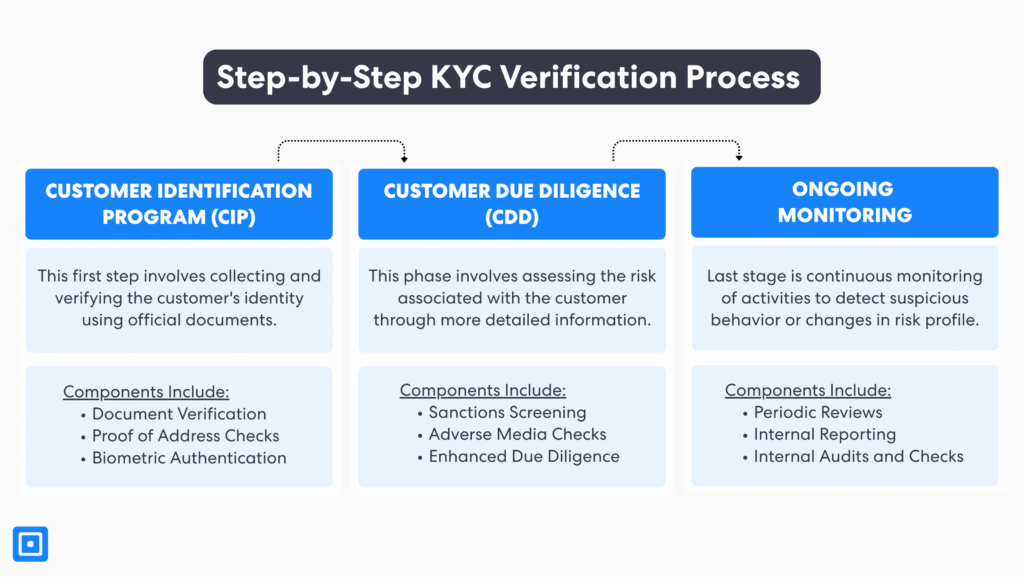
This section will provide a detailed overview of the specific stages and components typically found in the Know Your Customer verification process from a client’s perspective. The three key stages in a KYC process includes:
1. The Customer Identification Program (CIP): This first step involves collecting and verifying the customer’s identity using official documents. The components in this stage may include:
- Document Check: Organizations such as financial institutions will gather official government-issued identity documents from customers. These customer identification documents may include a driver’s license, passport, or birth certificate, which help to prove the customer’s identity.
- Biometric Authentication (optional): Many modern systems employ facial recognition technology to match a user’s selfie with their ID photo, preventing identity fraud. This verification can be performed live or through an uploaded image.
- Proof of Address Check: A Proof of Address (POA) check verifies a customer’s residential address. This step ensures that the client’s address matches their provided customer records. In POA checks, documents such as bank statements or utility bills are commonly used.
2. Customer Due Diligence (CDD): This phase involves assessing the risk associated with the customer through more detailed information. The components in this stage include:
- Sanctions Screening: To ensure customers are not prohibited from conducting financial transactions, they are screened against international sanctions lists and watchlists. This step helps businesses avoid facilitating illegal activities and ensures regulatory compliance.
- Adverse Media Checks: Reviewing news sources and public records to identify any negative information or red flags associated with a customer. This process helps uncover potential involvement in financial crime, fraud, or other illicit activities.
- Enhanced Due Diligence: EDD is especially essential for companies dealing with higher-risk customers, including Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) or those involved in complex business relationships. EDD builds on CDD, demanding further KYC documents, conducting deeper background checks, and continuously monitoring the customer’s financial transactions.
3. Ongoing Monitoring: The last stage is continuously monitoring activities to detect suspicious behavior or changes in risk profile. The components in this stage may include:
- Periodic Reviews: Establish regular updates for reviewing and reassessing customer information and risk profiles to detect any changes or new risks that may emerge over time.
- Internal Reporting: Set up an internal reporting mechanism on a company-wide level. Escalate suspicious activities or compliance issues within the organization for timely investigation.
- Internal Auditing: Conduct independent reviews of AML/KYC controls to ensure compliance and improve risk management strategy where necessary.
The Role of Technology in Modern KYC Procedures
Technology has transformed KYC solutions for banks and other financial institutions such that it is now feasible to achieve more effective and scalable compliance with KYC regulations and AML laws. Previously, traditional Know Your Customer (KYC) practices entailed strenuous amounts of paperwork and manual checks, which were slow and prone to inaccuracies. Today, electronic KYC (eKYC), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and blockchain are the focus of modern KYC compliance programs.
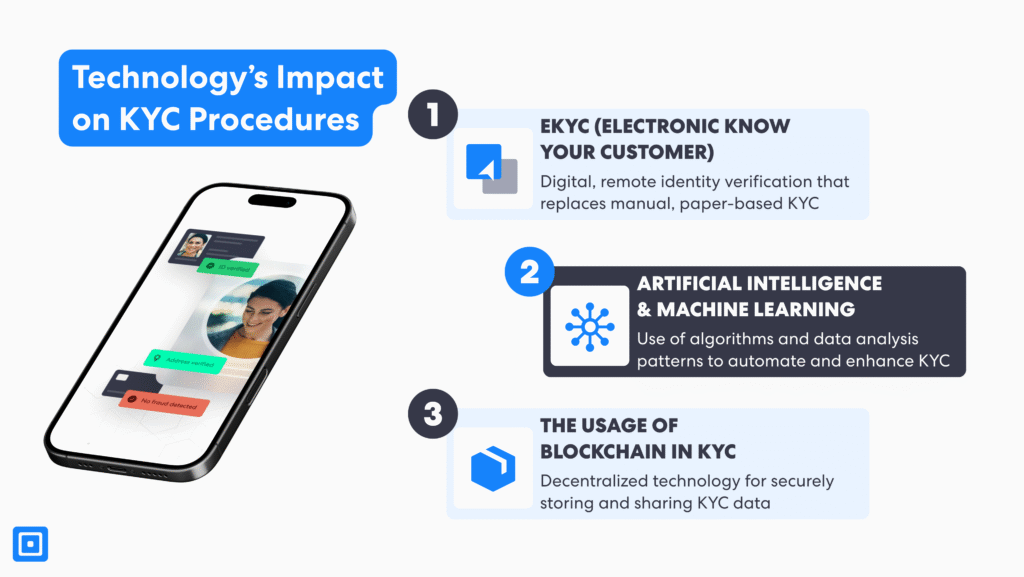
Electronic KYC (eKYC) and How It Prevents Money Laundering
Ekyc is the use of digital channels, including online channels, mobile apps, and biometric authentication, to name a few, to remotely and accurately validate a client. This digital process enables financial institutions to accurately validate people within a shorter time, reducing the cost of KYC compliance operations and onboarding time, while maintaining a positive consumer experience. eKYC supports financial systems in capturing, analyzing, and monitoring client information. In geographies with higher risk customers, the use of eKYC has led to enhanced risk assessments and regulatory compliance with real-time authentication.
Streamlining Customer Identity Verification with AI and ML
Artificial intelligence and machine learning have revolutionized KYC processes by automating data review, document validation, and risk assessment. AI and ML can analyze large amounts of data, detect counterfeit documents, and detect patterns of transactional behaviour that may signal money laundering or terrorism financing. AI-driven systems improve the accuracy of identity authentication, reduce the rate of false positives, and facilitate ongoing monitoring to ensure AML compliance. This enables compliance teams to deal with complex cases, improving the firm’s FinCrime prevention capability.
Upholding the Integrity of Financial Systems through Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers a transparent, impenetrable, and secure platform to store and exchange client identity data. By utilizing blockchain, banks can create impenetrable and decentralized digital identities, reducing the requirement to provide KYC documents repeatedly. It also makes the regulatory mandate less burdensome to meet without compromising data privacy. The transparency offered by using blockchain also supports enhanced audit trails and inter-institutional cooperation, maintaining the integrity of the world’s financial system.
Case Study: Binance Sanctioned in the Philippines
Problem:
In early 2025, the Philippine Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) launched an investigation into Binance, revealing that the crypto exchange had onboarded users without conducting proper KYC verification. Several high-risk accounts—including politically exposed persons (PEPs)—were found to have bypassed Customer Due Diligence (CDD) checks. The failure to monitor transactional behaviors raised regulatory red flags, particularly in light of the region’s updated AML guidelines under the Anti-Financial Crime Reform Act of 2024.
Solution:
Following the probe, Binance was fined PHP 50 million (~$900,000 USD). To rectify the lapses, Binance adopted a multi-layered compliance stack including AI-powered IDV tools, automated PEP and sanctions screening, and a new eKYC onboarding process aligned with FATF standards.
Outcome:
- Reduced onboarding time by 42% via eKYC automation.
- Achieved 100% PEP and sanctions list screening coverage.
- Strengthened AML audit readiness and restored regulator confidence.
- Rolled out compliant onboarding workflows across Southeast Asia.
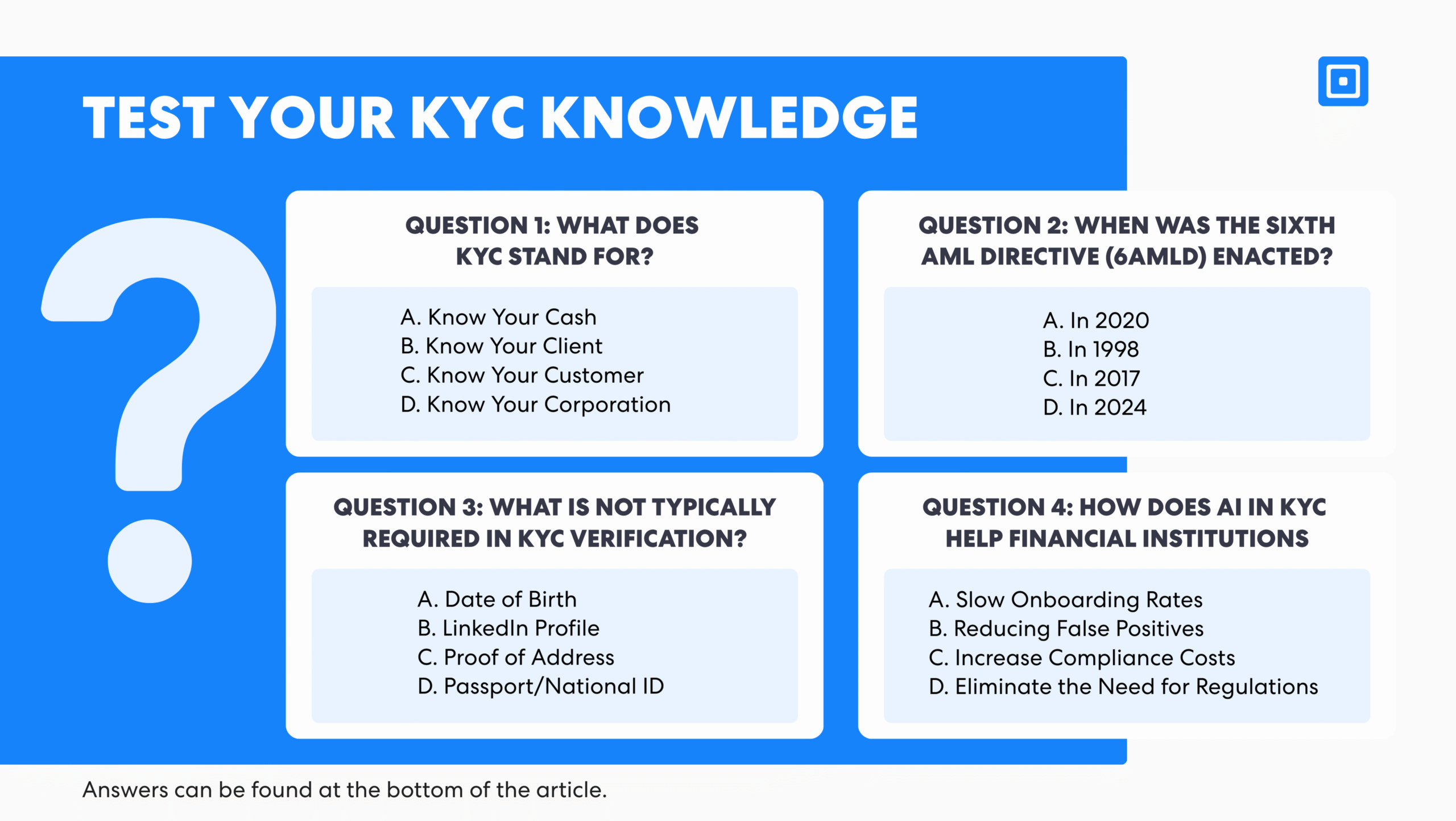
Test Your KYC Knowledge
Now that you’ve explored the essentials of KYC verification, it’s a good time to reinforce your understanding. Take a brief quiz below to test your grasp of the key KYC concepts, answers are provided at the end of the article.let’s take a quick break and put your knowledge to the test. Take the brief quiz below to assess your understanding of the key concepts for KYC. You’ll find the answers at the end of this article.
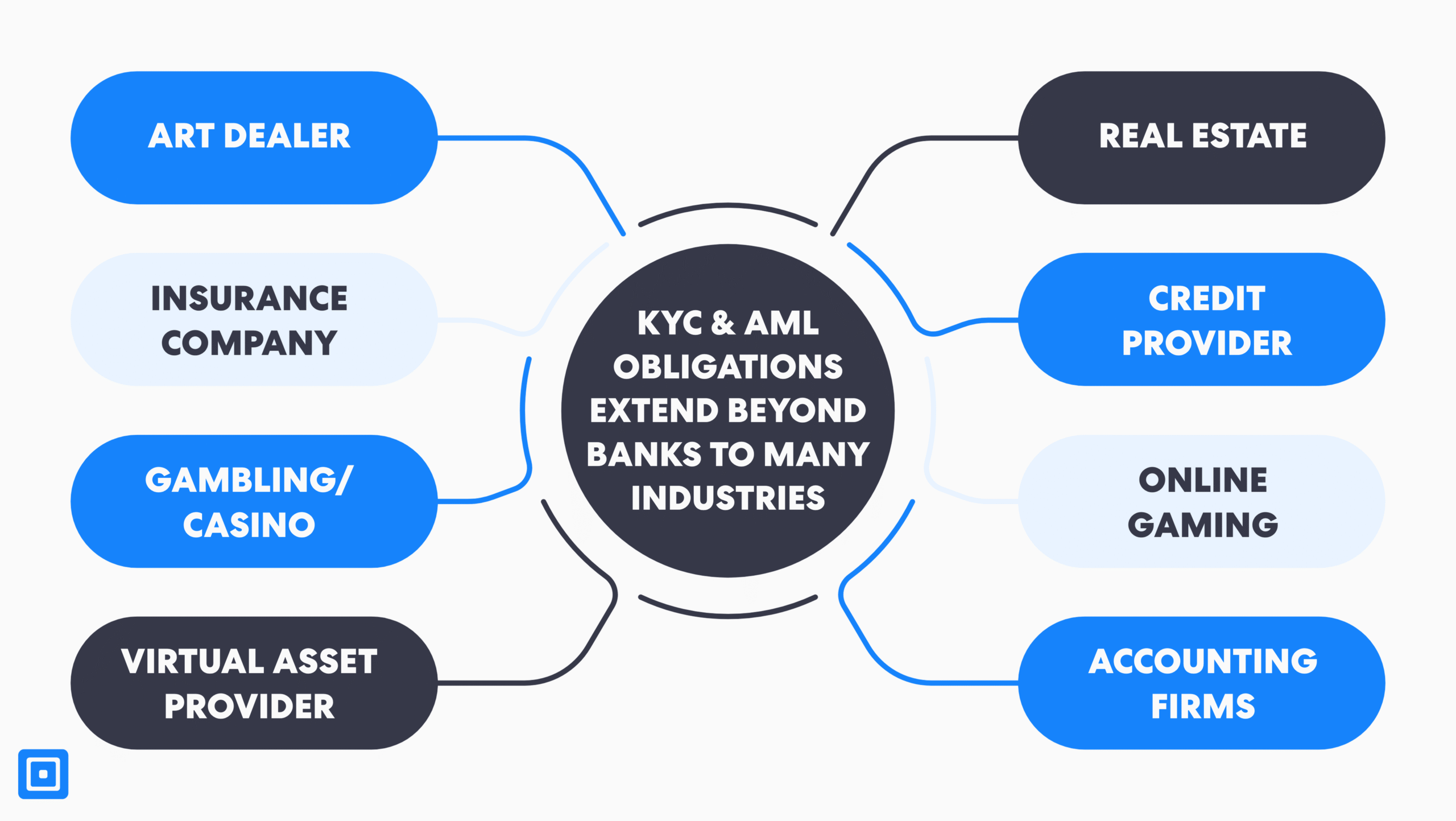
Is KYC and AML Compliance Only Subject to Financial Institutions?
As a result of financial crime risks beyond the banking sector, a growing number of high-risk industries are now legally obligated to uphold KYC verification requirements. Below are some of the industries where legal and regulatory evolution has encouraged the integration of KYC processes:
- Art Dealers
- Insurance Company
- Gambling/Casino Industry
- Virtual Asset Providers (VASPs)
- Real Estate
- Credit Provider
- Online Gaming
- Accounting Firms
Real Estate
Firms in the real estate sector have now embraced KYC due to its vulnerability to money laundering through property transactions and complex ownership structures. In the European Union, the 4th Anti-Money Laundering Directive (4AMLD) directly subjected real estate agents to AML and KYC in 2018, making them responsible for identifying clients and ultimate beneficial ownership before a transaction.
Online Gaming and Gambling
The gaming industry has witnessed increased demand for KYC to prevent fraud, underage play, and money laundering. AML Directives in the EU mandate online gaming sites to identify and authenticate a player’s identity, age, and geolocation and conduct transactional monitoring to detect unusual patterns. In the US, regulators impose stringent KYC requirements on gambling firms, compelling operators to implement robust customer authentication and verification measures.
Bitcoin and Digital Assets
Legislation targeting Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs), such as the 5AMLD, has subjected exchanges and wallet providers to KYC and AML compliance. Meanwhile, US regulators require cryptocurrency companies to register as money services businesses and comply with KYC and AML requirements. Such legal requirements ensure that digital assets are not used for illegal financial flows.
High-value dealers and other companies
Art traders, precious metal traders, and luxury goods traders are also subject to KYC requirements since valuable goods can be targeted for money laundering. For example, regulators now require precious metal and art traders to conduct due diligence on buyers when transactions exceed specified thresholds. Similarly, professional service firms such as law firms and accounting practices are legally obligated in many jurisdictions to identify beneficial owners and clients involved in high-risk transactions.
Key Takeaways
- Regulators mandate KYC verification to combat financial crime and prevent terrorism financing.
- The three phases of KYC verification are Customer Identification Program (CIP), Customer Due Diligence (CDD), and ongoing monitoring.
- Major global laws enforcing KYC include the BSA (US), AMLD (EU) and Federal Law No. 4 (UAE).
- AI, machine learning, eKYC, and blockchain now drive scalable, real-time KYC compliance.
- ComplyCube simplifies KYC with global coverage and continuous monitoring capabilities.
Empower Your Know Your Customer (KYC) Solutions with ComplyCube
KYC verification is no longer just a checkbox. It has become a vital process for protecting the integrity and trust of businesses worldwide. With strong Identity Verification (IDV) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) frameworks, firms can take a proactive risk-based approach to maintain alignment with evolving regulations.
ComplyCube is the award-winning, all-in-one compliance platform made and designed for businesses looking to streamline AML/KYC approach. Leveraging advanced, no-code technologies, ComplyCube makes client verification and onboarding rapid, accurate, and ready to scale with your organization. Get started for free today.
The correct answers are: C – Know Your Customer, A – 2020 for the sixth AML Directive (6AMLD), B – LinkedIn Profile as not typically required in KYC verification, and B – Reducing false positives as the benefit of AI in KYC.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does KYC verification involve?
KYC verification includes a structured process to confirm a customer’s identity and assess their risk level. It starts with collecting government-issued ID documents and proof of address, then moves into checks such as sanctions screening and adverse media monitoring. In higher-risk cases, Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is used. Finally, customer behavior is monitored continuously to detect suspicious activities and maintain compliance with AML regulations.
Is KYC required for all industries?
Not all, but many industries are now legally obligated to implement KYC verification due to increasing risks of money laundering and financial crime. These include banking, insurance, cryptocurrency, gambling, real estate, luxury goods trading, and accounting. Regulatory bodies like the EU and FATF have extended KYC mandates to cover these sectors, particularly when transactions involve large sums or complex ownership structures.
What is the difference between Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)?
CDD is the standard level of identity and risk checks applied to most customers. It includes document verification and sanctions list screening. EDD, on the other hand, applies to high-risk clients such as Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) or individuals from high-risk jurisdictions. EDD involves deeper background checks, source of funds verification, and frequent monitoring to manage elevated risks.
How does eKYC improve onboarding and compliance?
Electronic Know Your Customer (eKYC) allows businesses to verify customers remotely using digital tools such as biometric verification, AI-driven document checks, and secure online platforms. eKYC shortens onboarding times, reduces manual errors, lowers compliance costs, and enhances customer satisfaction—all while maintaining regulatory alignment and improving fraud detection accuracy.
How does ComplyCube support KYC verification?
ComplyCube simplifies KYC verification through its all-in-one compliance platform. It offers no-code onboarding workflows, real-time IDV, global document coverage, and automated screening tools. With capabilities such as biometric liveness detection, continuous monitoring, and advanced fraud prevention, ComplyCube helps businesses meet KYC requirements efficiently while scaling operations with ease.