Sanctions Screening tools are critical to strong Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) prevention, used to halt financial crime. Regulated businesses must conduct sanctions risk screening as a mandatory practice for effective sanctions compliance and ensure ongoing monitoring. Sanctions screening software and sanctions screening tools are a crucial component of the Know Your Customer (KYC) process, which ensures thorough due diligence within the sanctions check amid the growing demand for efficiency in handling transactions and regulatory requirements.
Sanctions screening is vital for financial institutions to comply with regulations and prevent money laundering. Using sanctions screening software with machine learning and natural language processing, institutions can efficiently identify politically exposed persons (PEPs) and entities in sanctions programs. Compliance requirements and regulatory compliance are essential aspects of this process. Risk management is also a critical factor in the context of sanction screening software. Ongoing monitoring, transaction screening, and alert management help reduce false positives and improve accuracy. Advancements in technology, such as robotic process automation and AI, are crucial for enhancing transaction processing efficiency and mitigating inefficiencies that arise from manual tasks. By integrating adverse media lists, a robust screening solution ensures compliance with requirements and mitigates financial crime risks. Additionally, institutions can tap into a comprehensive and dependable network of global sources to ensure the accuracy of screening lists.
As the sanctions landscape is ever-changing, understanding operational and regulatory implications is of paramount importance. This comprehensive guide aims to provide practical insights into sanctions, the governing bodies that enforce them, and the sanctions screening solutions available.
What are Sanctions?
Sanctions are tools used by countries or international organizations, enforced by regulatory bodies, to impose restrictions on certain activities or relations with specific regions, entities, or individuals. Sanctions enforcement is typically employed to address threats to national security or international peace, human rights abuses, and prohibit illicit activity. Sanctions can take various forms, such as financial restrictions, trade embargoes, and travel bans.
Some of the most prominent governing and sanctioning bodies include:
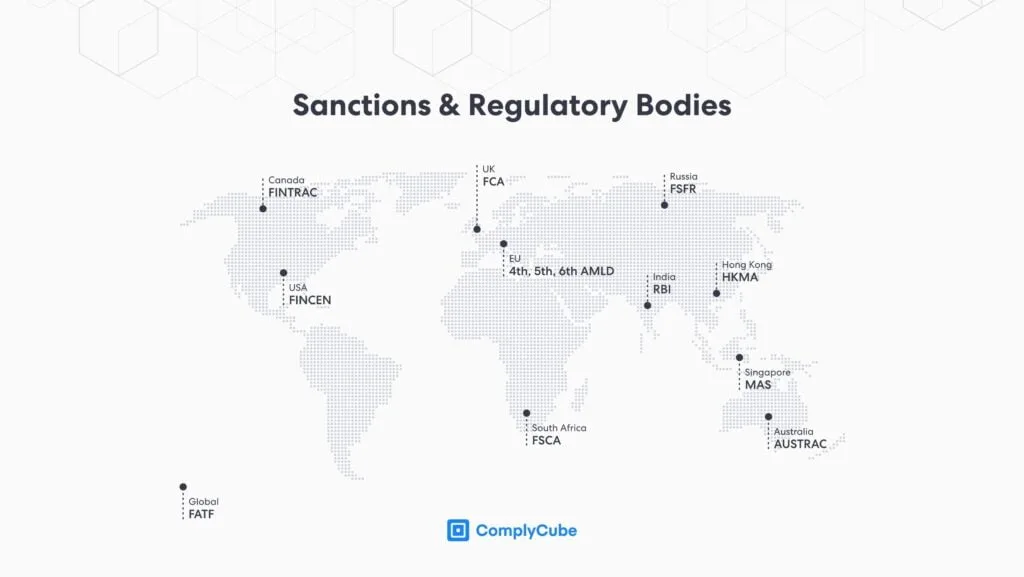
- United Nations (UN): The sanctions apply to all UN nation-states, encompassing a wide range of restrictions and measures.
- Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC): OFAC’s sanctions extend to all US citizens, individuals, and institutions conducting business within or connected to the United States and those engaged in transactions using US currency.
- European Union External Action Service (EU EEAS): The EU EEAS sanctions affect all EU citizens and legal entities established within any of the member states.
- His Majesty’s Treasury (HMT): This body oversees the United Kingdom sanctions list, which is applicable to individuals and legal entities working or conducting activities within the territory and under UK law. The Office for Financial Sanctions Implementation (OFSI) enforces these sanctions.
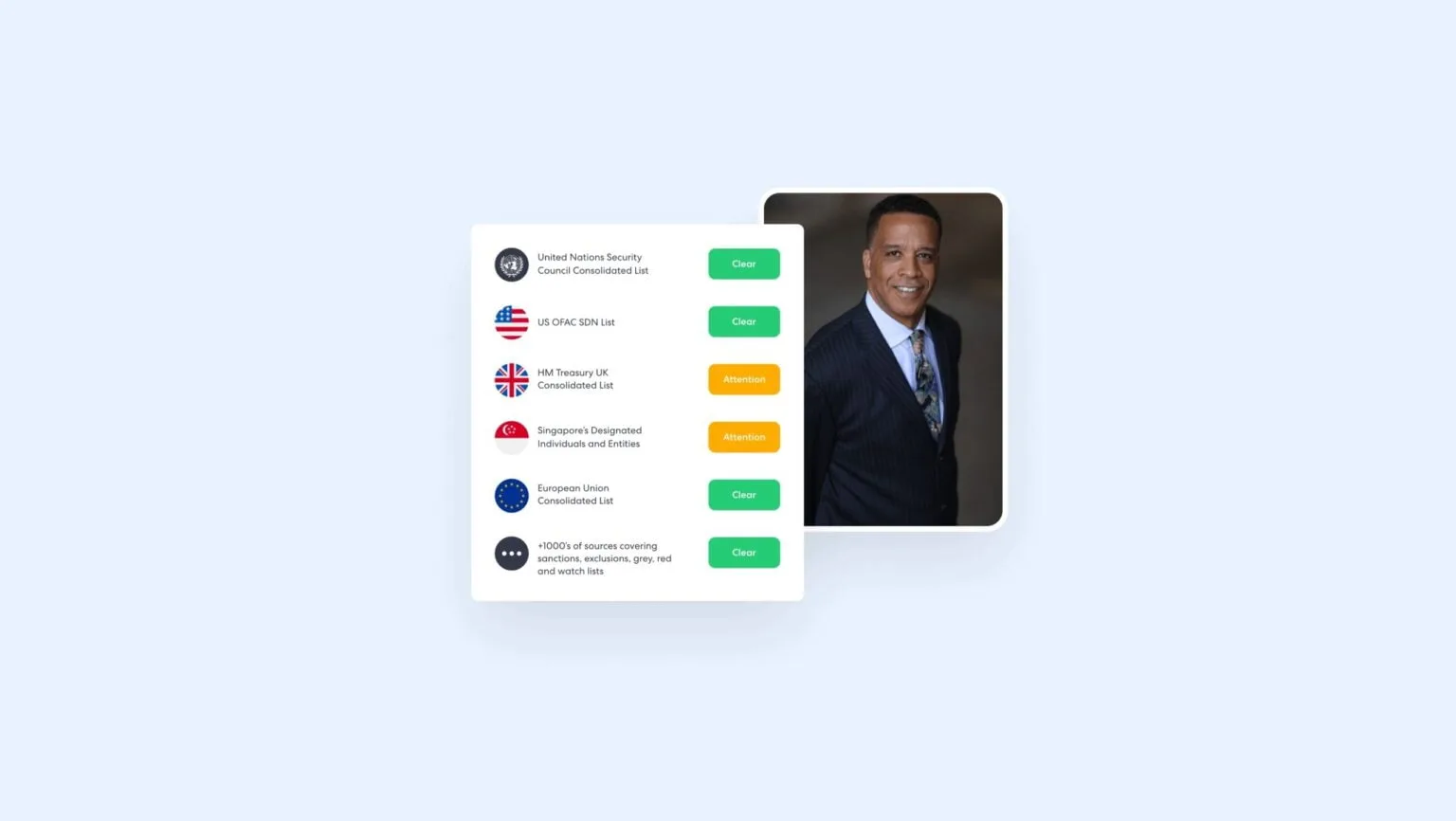
What is a Sanctions List?
A sanctions list is a publicly available document issued by national or international authorities such as the ones mentioned above. It is updated regularly and contains relevant details of individuals, entities, territories, or countries subject to economic or legal restrictions.
Individuals or parties identified on these sanctions lists may be denied access to financial systems, restricted from trade, or subject to other limitations as part of punitive or preventive measures.
Types of Sanctions
Sanctions compliance is not merely a legal obligation. Economic sanctions and trade restrictions play a crucial role in maintaining a secure and trustworthy business environment and prevent the facilitation of illegal activities such as terrorism financing, money laundering, and other financial crimes.
Restrictions can be applied on different levels:
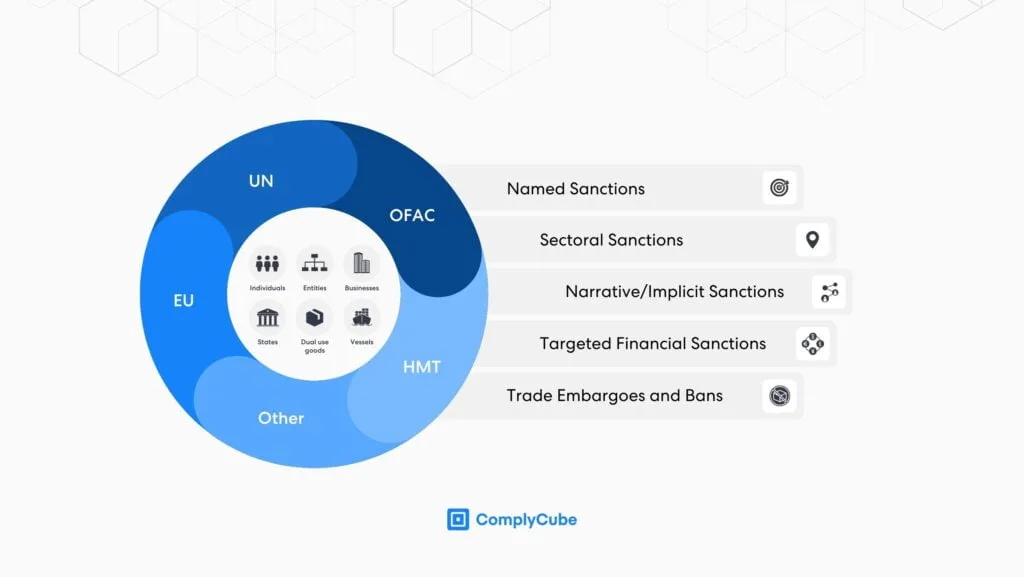
- Explicit sanctions name the subject directly, be it an individual, entity, or country.
- Narrative or implicit sanctions don’t specifically name an individual or an entity. Instead, the narrative implicitly covers them due to their connections to a named sanctioned body or sector.
From an economic perspective, sanctions can materialize into:
- Comprehensive sanctions: imposing restrictions on all transactions with a specific country. Some examples include Iran, Cuba, and Sudan.
- Targeted sanctions: limiting transactions with specific individuals, entities, or individuals listed on the Specially Designated Nationals and Blocked Persons (SDN) list maintained by OFAC. Russia is a prime example.
- Sectoral sanctions: designed to hinder the future development of specific sectors within an economy by prohibiting a specific subset of financial transactions related to those sectors.
Understanding Sanction Screening Software
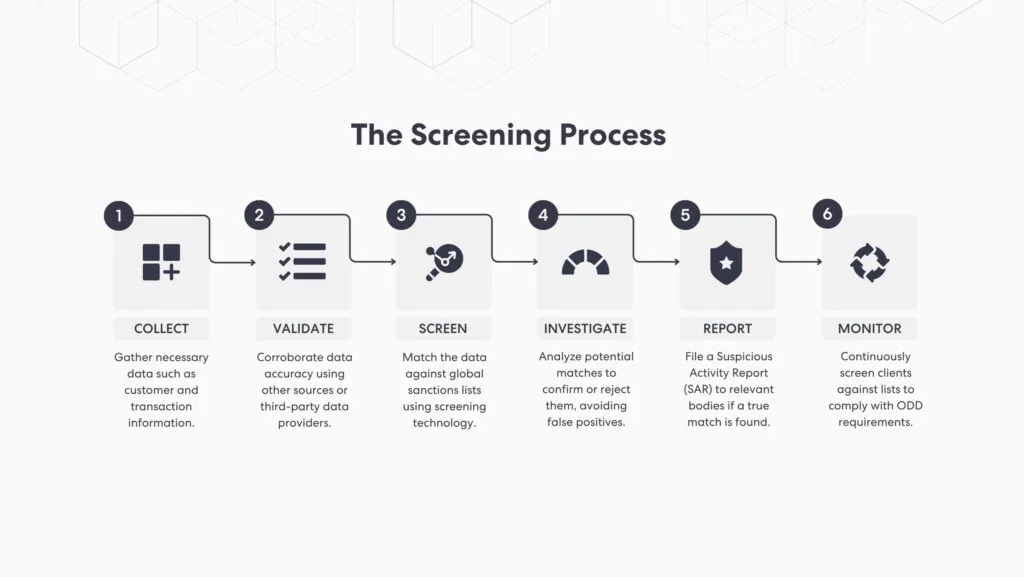
Sanctions screening is a critical component of an effective AML/CTF program, driven by the demand for financial institutions to meet heightened expectations for compliance and enhanced operational controls. It involves checking an organization’s existing and potential customers, partners, and transactions against global sanctions lists to identify financial risks and ensure compliance with international regulations. The process typically involves six key steps utilizing advanced screening technology and transaction screening methods:
Step 1: Collect
The first step involves collecting necessary data that will be checked against a sanctions list. This typically includes information about customers, potential business partners, and transactions. The data collected may include names, addresses, dates of birth, nationality, and other pertinent details to ensure data accuracy.
Step 2: Validate
Once the data is collected, data validation is crucial to corroborate the information and ensure its accuracy. This step often involves cross-checking the data against other sources, such as ID documents, company registers, or third-party data providers. The goal here is to ensure the integrity of the data before it is used in the sanctions screening process.
Step 3: Screening Solution
After the data has been collected and corroborated, it’s time for the actual screening process. Using sanctions screening technology, the collected data is matched against global sanctions lists, which include individuals, organizations, or countries that are embargoed or sanctioned by regulatory bodies.
Step 4: Investigate
If a potential match is identified during the sanctions screening process, it triggers an investigation process. The analysis aims to confirm or reject the potential matches upon enriching the client data and cross-checking the details. This step confirms whether the alerts were false positives or true matches.
Step 5: Report
Reporting is the final and optional step in the sanctions screening process, activated only if a true match is found. The institution must adhere to reporting requirements and file the Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) to the relevant authority following the proper protocols, as failing to report a match can lead to severe penalties.
Step 6: Monitor
An essential, often overlooked step in the process is continuous monitoring. Regulations and sanctions lists are dynamic. Continuous monitoring can be done in real-time or periodically to ascertain compliance with ongoing due diligence obligations.
When Should Sanctions Screening be Performed to Ensure Compliance?
Sanctions screening should be performed at several key stages to maintain compliance, including ongoing monitoring. The initial screening has to take place when onboarding a new client or partner. Before engaging in business transactions, financial institutions or businesses must verify the identities of their clients or partners against relevant sanctions lists. This step ensures that the entity or person is not barred from engaging in certain activities.
However, performing sanctions screening and risk assessments only at the start of a business relationship is insufficient. It should happen regularly throughout the customer relationship lifecycle. This is because sanctions statuses can change over time. A customer who was not a sanctioned party during onboarding or initial risk assessment might become one later.
Case Study 1: Rusal
A notable example of how changes in sanctions lists can impact businesses is the case of Rusal. This major aluminum producer was added to the US Department of Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) list in April 2018 due to its association with Russian oligarch Oleg Deripaska.
The abrupt addition had a significant effect on global aluminum markets. Corporate entities around the world, involved in ongoing or future contracts with Rusal found themselves needing to halt all trading activities immediately. This step was necessary to comply with the new sanctions and avoid potential fines, highlighting the importance of regular monitoring of sanctions lists.
The company was later delisted in early 2019 when its founder, entrepreneur Oleg Deripaska, consented to forfeit control, lifting sanctions from the aluminum manufacturing company. This case reaffirms that continuous monitoring is vital in ensuring adherence to the ever-changing sanctions landscape.
Identifying Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) and Their Role in a Sanctions Check
Politically exposed persons (PEPs) are high-risk individuals who hold a prominent public role or have a close association with such individuals. Due to their position and influence, PEPs pose a higher risk of being involved in bribery, corruption, money laundering, and other financial crimes.
Identifying and conducting enhanced due diligence on a politically exposed person is critical to an effective sanctions screening process. Organizations should have robust PEP screening controls in place to mitigate associated risks. These controls should include regularly checking customer data against PEPs lists and transactional screening to identify suspicious activities.
You can learn more here: What is a Politically Exposed Person (PEP)?
Case Study 2: Isabel dos Santos & PwC
For instance, in 2018, Isabel dos Santos, the daughter of Angola’s former president and identified as a Politically Exposed Person (PEP), came under scrutiny when leaked documents suggested she exploited family connections and public funds to build her $2 billion fortune. Her PEP status made her high risk for banks and other institutions due to the increased chance of potential involvement in bribery or corruption.
PwC, a renowned global accounting firm, found itself in hot water over its involvement with Isabel dos Santos and her financial misconduct. During the time under criminal investigation, PwC had been auditing Sonangol’s books, Angola’s state-owned oil company.
However, the firm’s dual role as an advisor on a significant restructure for Sonangol has been criticized for presenting a potential conflict of interest. The auditing and advisory work by PwC took place while dos Santos, who had already been identified as a PEP, served as the chair of Sonangol.
Dos Santos was relieved from her role shortly after her father’s retirement, and the new management at Sonangol subsequently terminated PwC’s contract early, replacing it with KMPG. This case highlights the considerable risks and potential complications firms can face when dealing with PEPs.
The Impact of Adverse Media on Sanctions Screening
Adverse media, also known as negative news, refers to information from various media sources that indicate potential sanctions risks associated with certain customers or business partners. It is a crucial component of an effective sanctions screening program as it can provide early warning signs of possible sanctions.
For instance, news about a customer’s involvement in illegal activities, association with sanctioned parties, or changes in their political or business status can indicate probable threats.
Adverse media screening should be performed regularly and at various stages of the customer relationship lifecycle. Organizations should leverage advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and natural language processing to automate and enhance this process.
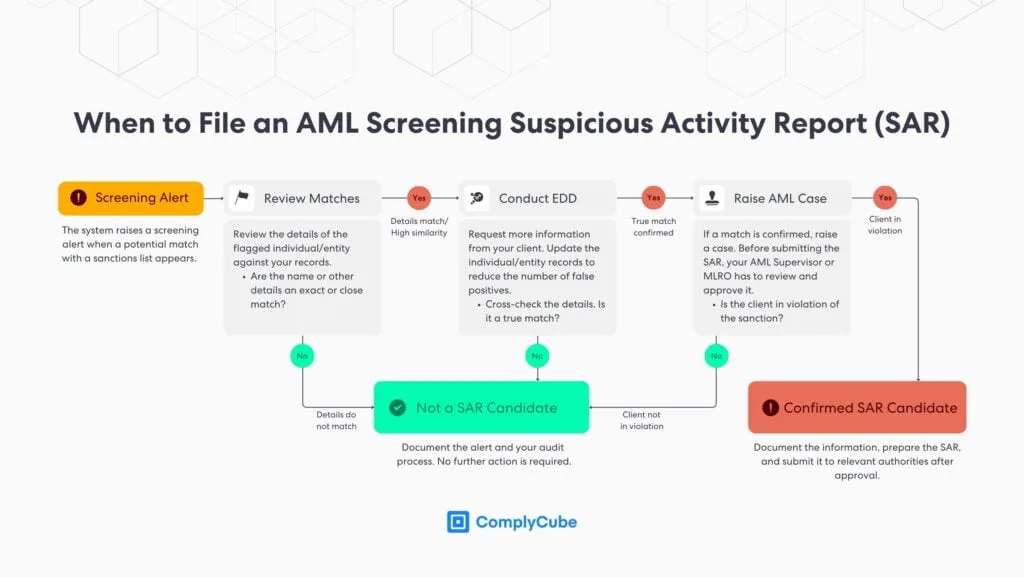
Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs)
Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) are crucial in sanctions screening, providing financial institutions with a means to report potential illicit activities. When transactions raise suspicions of violations, institutions file SARs with competent authorities. These reports facilitate investigations by law enforcement agencies, enabling them to take necessary actions.
According to Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), financial institutions in the US are experiencing a significant surge in the submission of Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs). In 2022, the total number of SARs filed exceeded 3.6 million, marking a substantial 57% increase compared to pre-pandemic levels in 2019.
SARs contribute to the collective fight against money laundering, helping protect the integrity of the financial system. Financial institutions avoid enforcement actions and assist regulatory organizations and law enforcement agencies in their mission by detecting and reporting suspicious activities.
Consequences of a Sanctions Breach
Failure to comply with AML regulations and sanctions screening requirements can result in severe compliance penalties, including punitive fines, criminal proceedings, damaged reputation, and sanctioning.
For instance, breaches of financial sanctions in the UK are criminal offenses punishable by up to 7 years in prison and monetary fines levied on individuals and businesses found in breach. Similarly, the US Treasury Department’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) considers sanctions violations a grave threat to national security and foreign relations. Consequently, offenders face monetary fines of up to several million dollars and prison time of up to 30 years. Several firms were heavily fined for OFAC breaches, in some cases exceeding $1 billion. These include ZTE, Standard Chartered, BNP Paribas, Crédit Agricole, Société Générale, and UniCredit. All these consequences can seriously damage an institution’s reputation, credibility, and performance. Becoming a sanctioned entity can be even more damaging, as it significantly hinders, if not halts, an institution’s ability to conduct global business and access international markets and capital. In some instances, these consequences led to a sanctioned institution’s complete inability to continue operations and, ultimately, its demise.
Several firms were heavily fined for OFAC breaches, in some cases exceeding $1 billion. These include ZTE, Standard Chartered, BNP Paribas, Crédit Agricole, Société Générale, and UniCredit.
In summary, sanctions breaches constitute serious offenses and thus have a severe impact. Therefore, institutions must efficiently screen customers against relevant sanctions lists. However, as sanction lists are constantly updated, it is crucial to ensure that sanctions screening processes keep up with changes while avoiding inefficiencies and reducing false positives.

What are the Challenges Facing Sanctions Screening?
Sanction Screening has never faced as many screening challenges as it does today due to several factors, including:
- Sanction lists are evolving rapidly in nature (e.g., narrative sanctions) and breadth (e.g., US technology export controls).
- Increase in the complexity of restrictive and punitive sanction measures and screening regulations.
- Sanction Screening has to account for association risk, which may not be immediately apparent. For instance, the Patriot Act forbids US corporations from supplying ‘financial assistance’ to organizations accused of terrorism.
- Multiple sanctioning bodies have different standards and agendas that do not align, leading to inconsistent economic sanctions.
According to the data company Refinitiv, as of early 2020, there were more than 34,000 explicit sanctions across more than 280 sanction programs, with an increase of 62% since September 2017.
Choosing the Right AML/KYC Sanctions Screening Partner
Despite the inherent challenges of Customer Screening, the right AML/KYC partner can help you implement a robust and cost-effective solution, as outlined below.

Single Customer View
Sanctions Screening is only as effective as the input data used to screen the entity or individual at hand. Therefore, it is recommended to leverage a solution that will help you streamline data collection processes and provide you with a single customer view that is aggregated, consistent, and holistic through data aggregation.
Comprehensive Data Coverage
Screening activities should build on thoroughly studied and regularly revised global risk information that includes comprehensive data coverage of the current PEP and sanctions lists, unfavourable media, and compliance reports from around the world.
Smart Screening
Numerous vendors market fuzzy name matching as a silver bullet for state-of-the-art sanctions screening. However, fuzzy name matching should not be solely relied upon. It does indeed account for misspellings and minor variations.
However, it does not deal well with phonetic similarity, transliterations, linguistic variations, non-Latin scripts, patronymics, honorifics, titles, or out-of-order names, to enumerate a few of the aspects of a reliable screening engine needs to take into account. ComplyCube offers a comprehensive sanction screening solution.
Risk-based Approach
Risk-based approach (RBA) is a comprehensive sanctions screening solution should manage several sanctions lists and allow custom thresholds and inclusion/exclusion rules to enable AML officers to adapt the screening capability to the organization’s risk perception and policies.
You can learn more about the topic here: What is a Risk-Based Approach (RBA)?
Case Management
AML case management, combined with monitoring and alerts, enables analysts to investigate suspicious activity and quickly mitigate financial crime risk effectively. A robust Case Management solution should also provide a fully integrated experience with rich contextualized data, such as a detailed match breakdown, and thus help investigators organize, prioritize, manage investigations, and easily discount false positives – all while creating a permanent audit trail for regulatory review.
Ongoing Due Diligence
Depending on the customer and your risk mitigation strategy, you may need to include sanctions screening monitoring and alerts. Many AML/KYC vendors can check customers in bulk via running batches. However, that is a cumbersome and reactive process unsuitable for the new digital age. On the other hand, mature KYC providers will offer ongoing monitoring to support the shift from the traditional tick-the-box approach to real-time, ongoing, and proactive customer due diligence.

Sanctions Screening Software for Financial Institutions
In the ever-evolving world of finance, sanctions screening has emerged as a non-negotiable requirement. At its core, it represents an integral part of the financial sanctions implementation mechanism used globally. This process is critical to ensure that entities like banks and other financial institutions do not engage in business transactions with individuals, organizations, or countries that are on global sanctions lists.
Financial institutions worldwide implemented robust sanctions screening software to aid their compliance efforts. The importance of sanctions screening within the financial industry cannot be overstated. It’s a crucial measure to mitigate the risk of engaging with sanctioned entities and to prevent money laundering.
As OFAC’s enforcement penalties hit new records year after year, the cost of non-compliance has never been higher. As such, financial services companies should continually refine their sanctions screening processes and stay ahead of evolving global sanctions landscapes to effectively navigate this complex regulatory environment.
Implementing a Strong Sanctions Check
Sanctions screening serves as an indispensable component in maintaining a compliant and secure financial environment. By vigilantly cross-checking customer data against sanctions lists provided by regulatory bodies such as the United Nations and the European Union, businesses can prevent transactions with sanctioned parties. This proactive stance strengthens Anti-money Laundering (AML) efforts and contributes to the broader global initiative to prevent financial crime.
The world of sanctions and Anti-money Laundering compliance is continually evolving, and maintaining an up-to-date sanctions list at the heart of your screening processes is essential to navigating this complex landscape effectively. Choosing the right AML/KYC and sanctions screening partner, such as ComplyCube, can also provide significant benefits.
Explore our global PEP and Sanctions screening solution to learn more about our platform!