Fintech companies are widely known for adopting advanced technological capabilities, enabling them to develop services that operate at rapid growth, speed, and scale. While this is the main reason the sector is highly competitive and successful, it also opens the door to money laundering and financial crime risk. This guide delves into the importance of Anti-Money Laundering (AML) processes, the latest fintech AML regulations, and the biggest challenges in fintech and compliance.
The Critical Role of Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Solutions in Fintech Companies
The fintech industry creates the perfect space for criminals to engage in terrorism financing, identity theft, and even drug trafficking. This is why there is an increasing requirement for businesses in the sector to leverage strong fintech AML processes:
- Compliance Obligations: Regulatory bodies increasingly enforce regulatory requirements on wider sectors, not just traditional banks. Legislation such as the US Bank Secrecy Act and the Sixth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (6AMLD) requires fintech companies to implement effective AML and KYC compliance solutions.
- Build a Safe Ecosystem: Fintech companies that prioritize building a secure environment gain the trust of customers, business partners, and regulators. Integrating a compliance culture is key to preventing data breaches and financial losses. Plus, it strengthens the company’s reputation as a trustworthy player.
- Remain Competitive: The fintech industry is highly competitive, and businesses choose to remain agile and flexible to attract customers and investors. Aligning with stringent AML compliance enables firms to combat money laundering effectively and avoid reputational risk.
- Long-Term ROI: Adopting modern regtech solutions and AML software supports fintech companies by removing manual tasks prone to human error. As a result, organizations can expect higher cost savings, enhanced customer relationships, and long-term competitiveness.
Key Regulations for Fintech AML in 2025
Global AML compliance standards are often updated frequently to close the gaps that arise from technological and financial innovations. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is a global organization founded in 1989 by the G7 nations to develop policies to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing.

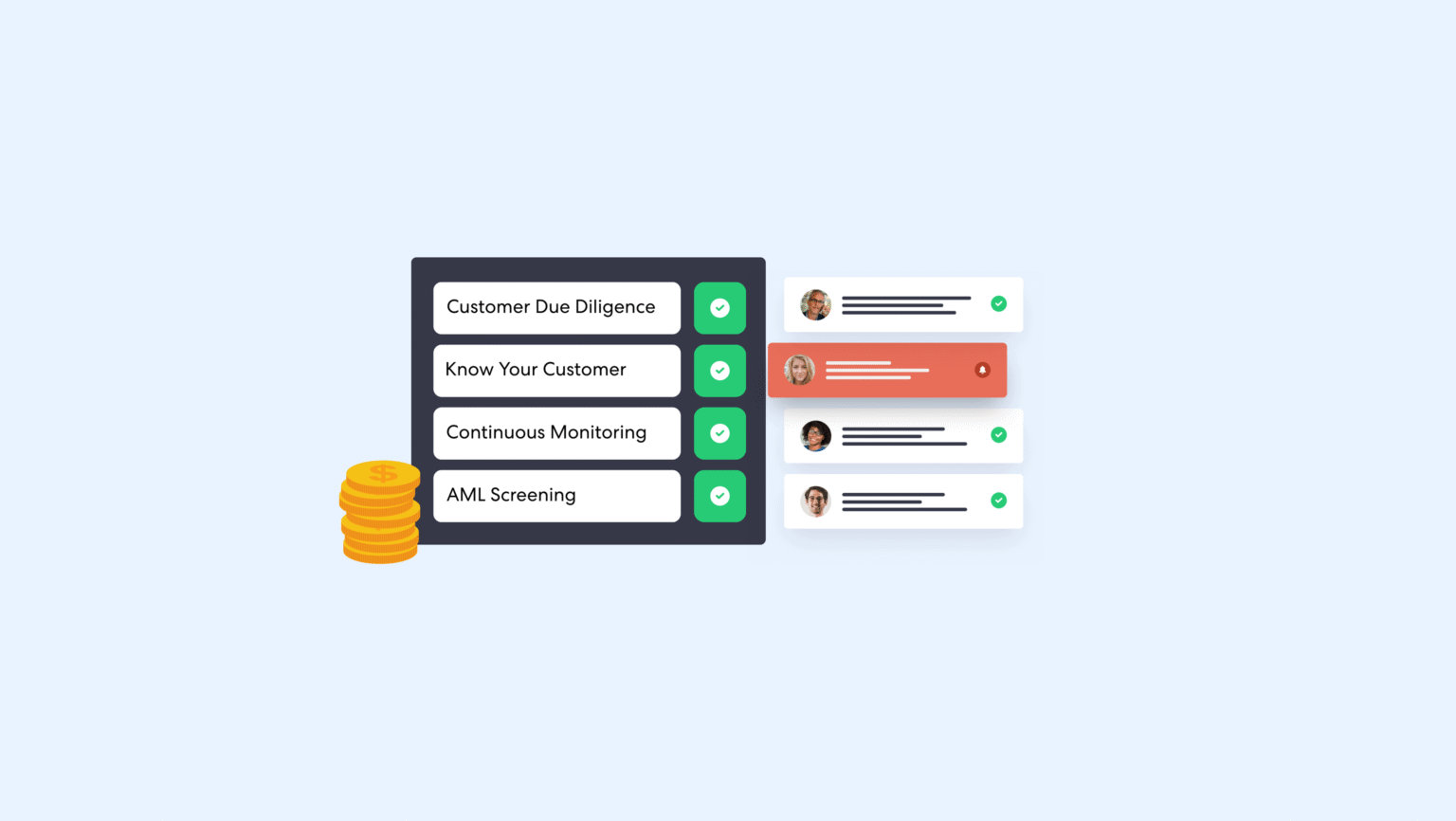
The FATF mandates that businesses within the financial sector or those providing financial transactions implement a strong risk-based approach, enhanced due diligence, and ongoing AML monitoring. The most critical compliance processes for fintech companies to comply with FATF recommendations include:
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and KYC
Fintech companies must perform thorough Know Your Customer (KYC) and Customer Due Diligence (CDD) checks. The process includes leveraging strong identity verification tools to verify customer identities, assess customer risk profiles, and perform ongoing monitoring. To achieve full regulatory compliance, businesses must execute enhanced due diligence for high-risk users and countries.
Continuous Monitoring and Real-Time Verification
More responsibility is placed on businesses to identify suspicious behavior through ongoing monitoring and real-time transaction verification. Fintech companies must be able to detect suspicious patterns, flag high-risk transactions, and file Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) promptly.
Sanctions and PEP Screening
Advanced AML screening capabilities must be adopted to screen customers against global sanctions lists and Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) databases. Proactive risk management is vital to prevent high-risk clients from accessing sensitive information and keep existing customers safe from potential criminal financial activities.
Clear Reporting and Auditing Trails
Many jurisdictions now require fintechs to obtain specific licenses or register with local authorities as part of AML oversight. Clear data privacy laws, internal controls, robust reporting, and transparent auditing trails must be implemented to support compliance efforts.
Company-Wide Training on AML Obligations
Frequent AML training for all staff is mandatory, ensuring awareness of regulatory changes, new money laundering techniques, and internal procedures. Strong corporate governance and a compliance-first culture are essential to meeting regulatory expectations and avoiding enforcement actions.
The Common Challenges in Fintech and Compliance
Financial institutions and fintech firms face many challenges when implementing effective AML programs. If not navigated well, these challenges can lead to dire unintentional consequences, including facilitating illicit funds, tax evasion, suspicious transactions, and other financial crimes.
Fintech AML challenges are unique and multifaceted:
- Changing Regulatory Landscape: Fintechs and financial institutions alike face evolving AML laws and strict regulatory compliance demands. A lot of time and resources are spent monitoring compliance processes and maintaining an effective AML program.
- Rapid Cross-Border Activities: With globalization, large financial transactions are happening rapidly across countries. Transaction monitoring and fraud detection are becoming tougher daily, with AML risks on the rise.
- Digitalization of Identity Verification: Identity verification and customer due diligence can now be done digitally. While this brings operational efficiency, money launderers can exploit multiple accounts or use stolen identities online, raising customer risk.
- High Cost: Most fintech companies operate a lean and agile framework for cost-effectiveness. Having robust transaction monitoring and risk management tools can be harder to expense compared to larger financial institutions.
- Sophisticated Criminal Tactics: Relying on legacy and traditional rule-based systems is insufficient to meet Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations. Businesses must adopt modern, effective AML compliance tools to outpace criminals.
What are Popular AML Compliance Failures in The Fintech Industry?
Although most fintech companies may agree that AML compliance is a competitive advantage, it can be detrimental if not properly implemented. Here are some examples:
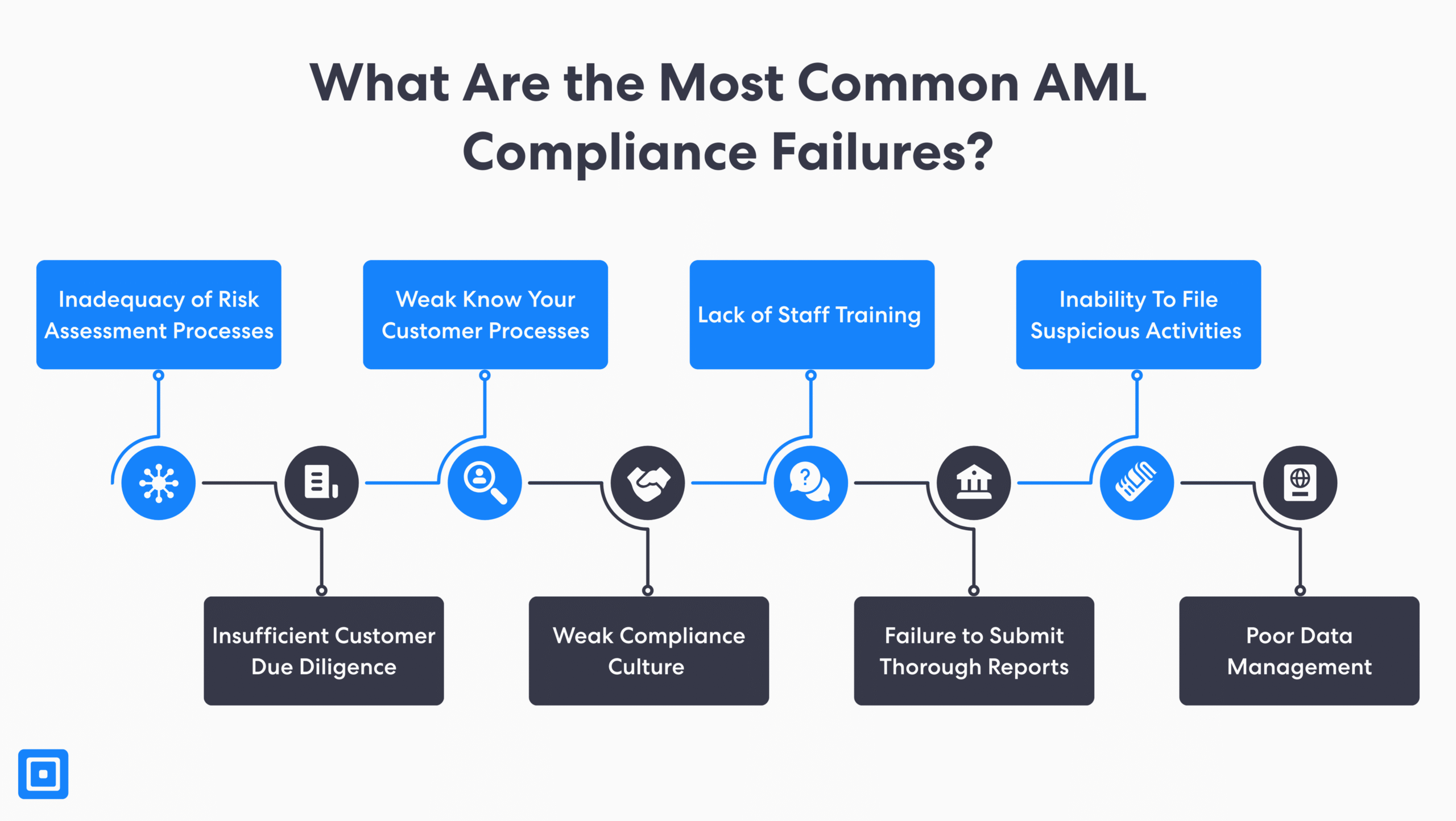
Case Example 1: KuCoin’s 2 Year Forfeit from the US Market
KuCoin, the global cryptocurrency exchange firm, was fined almost $300 million and had to exit the US market for two years. The heavyweight fintech company, launched in 2017, was fined for its poor AML controls and KYC regulations. This included failing to comply with the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and its requirements for registering as a money transmitting business.
Case Example 2: Ratepay faced with nearly €25,000 in fines
Ratepay, a leading German fintech founded in 2009, was fined €25,000 (approximately $28,260) by BaFin for anti-money laundering (AML) compliance breaches. The regulator cited Ratepay’s failure to submit adequate suspicious activity reports and transaction data. Additionally, the company had weak internal controls and suspicious transaction monitoring systems.
Case Example 3: Coinbase Group hit with $4.5 million fines
Coinbase Group, under the CB Payments Limited (CBPL), faced massive losses of £3.5 million (about $4.5 million) in fines. The Financial Conduct Authority in the UK charged the company for its poor financial crime control framework. Moreover, Coinbase failed to implement strong anti-money laundering (AML) compliance, transaction monitoring, and fraud detection processes.
Best Practices for Fintech AML Compliance with the U.S. FinCen
The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) is the U.S. regulatory body that delivers recommendations for AML compliance. While FinCEN’s guidance is centered on the U.S. financial system, it is widely referenced by financial institutions on a global scale:
- Risk Appetite Management: Firms are encouraged to adjust their AML controls to align with their risk appetite. A risk-based approach with more resources on higher-risk customers enables compliance while maintaining operational efficiency.
- Data Sharing Initiatives: FinCEN strongly recommends that financial institutions share information with one another about suspected illicit funds and suspicious activities. Businesses can expect a more coordinated and holistic response to money laundering and terrorism financing.
Regulatory Outlook: What’s Next for Fintech AML?
Fintech AML in 2025 seeks to strengthen how financial institutions combat money laundering, financial crime, and terrorist financing. Integrating a strong compliance culture first builds a proactive team that identifies and reduces AML risks. Moreover, teams that adopt AI and Machine Learning (ML) can expect rapid and accurate identity verification and KYC. By following the best practices and latest AML regulations, fintech companies can remain agile and strong in the face of evolving regulations and avoid hefty fines.

Get started with strong AML and KYC processes with advanced risk management and ongoing monitoring capabilities. Speak to a member of the team today.