TL;DR: Digital identity solutions lower fraud while meeting customer expectations for fast online services. A digital identity check evaluates risk signals to verify identity in real time, while digital identity validation proves the identity data is trustworthy and consistent. Together, they support comprehensive digital identity verification that helps businesses prevent fraud.
What are Digital Identity Solutions?
Digital identity solutions are tools, workflows, and controls that help an organization verify someone’s identity online. This way, genuine customers can access services safely. They combine documents, biometrics, and reviews against data sources to confirm that a person is who they claim to be.
As a result, these solutions make identity into a clear, measurable control to support consistent decisions and traceable outcomes. A strong digital identity verification process is vital in fraud prevention scenarios. Today’s traditional methods simply cannot keep pace with the scale and automation capability of evolving attacks.
How Digital Identity Checks Work
In today’s world, fraud comes in the form of fake personas and reused stolen identity information. They do this by testing services using the same device, different phone numbers or a reused email address. They thrive off of finding gaps within the verification process in order to exploit them for gain. This threat of fraud only creates constant pressure for systems controls.
Customer expectations are rising at the same time. People want a quick onboarding process with mobile device capture. They also expect minimal friction from start to finish. Businesses must prevent fraud and deter fraudulent activity while helping a genuine person easily prove they are legitimate. Getting this balance wrong can increase drop-off or increase risk.
Core Blocks of Digital Identity Verification
There are three types of evidence when it comes to digital identity verification. The evidence often covers what a person has, what a person is, and what a person controls. Documents are analyzed for authenticity and signs of tampering to prevent fraud. Biometrics and liveness detection as well as multi-factor authentication come together as the core blocks. These elements provide fraud protection without forcing users and customers into manual identity verification. You can learn more here: What to Look for in a Biometrics Identity Verification System
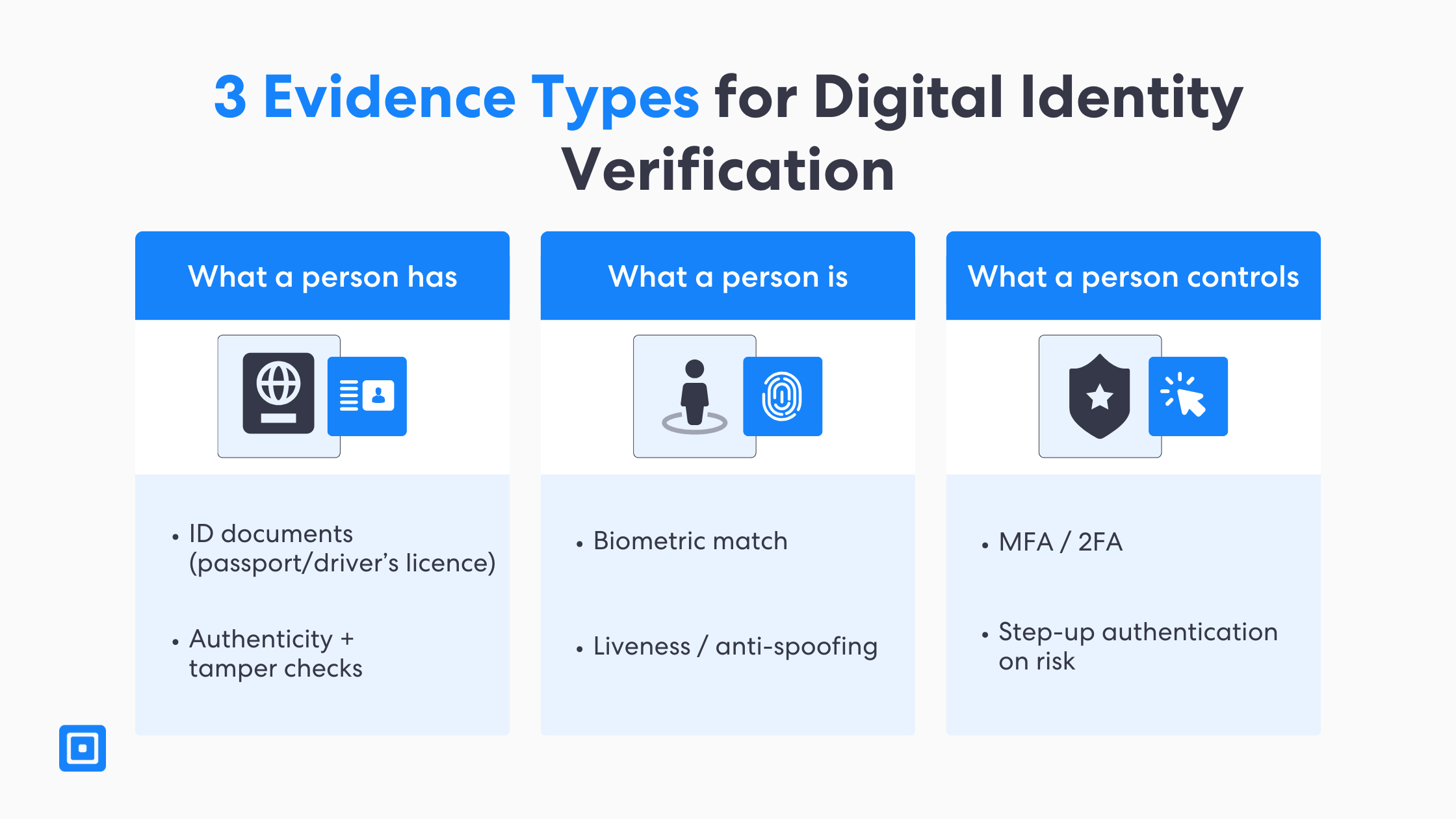
Authoritative standards and guidance increasingly frame this as risk-based. For example, NIST’s Digital Identity Guidelines cover identity proofing and authentication requirements that organizations can use to match assurance to risk. This approach helps teams apply stronger checks only when the context and fraud risk justify them.
Evidence in digital identity solutions
Evidence is the starting point for most digital identity verification solutions. Most platforms start with ID documents, such as passports or driver’s licenses, and then focus on testing document authenticity. They look for evidence through signs of data tampering, and confirming that key fields match the correct formats. Additionally, some flows can incorporate facial recognition with liveness detection to confirm whether users are real in the moment.
Finally, digital identity solutions platforms enrich decisions with more important and contextual data. This other data includes device intelligence signals, behavior, geography, and transactions. Bringing in automated processes makes it easier to spot patterns across many attempts. Identifying such a pattern happens much faster than through separate data points in manual verification. It also keeps controls audit-ready by providing logs, inputting rules, and reason codes. Decisions are now easier to review and will improve faster over time.
Digital Identity Check vs. Digital Identity Validation
There are two types of digital identity solution; digital identity check and digital identity solution. A digital identity check reflects a real-time decision that answer the question, “Should a user get access?” It does this by combining relevant evidence, assessed risk signals and checking against policy rules. This brings a user to a few different outcomes; pass, fail or step up to enhanced due diligence. The decision based on the level of fraud risk that comes across in the onboarding session.
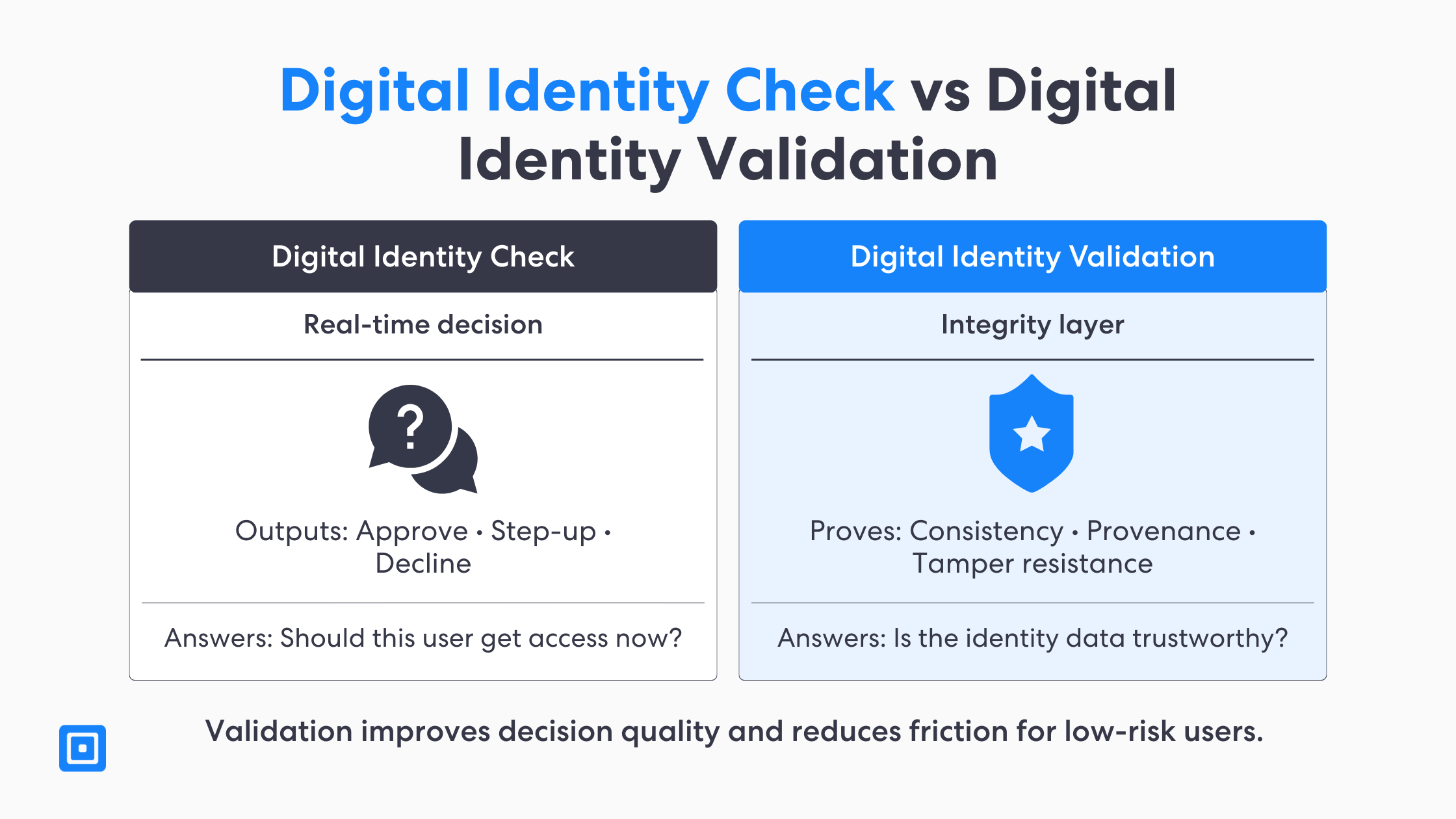
Digital identity validation is more specific than a basic check. It answers a clear question: “Is the identity data and evidence trustworthy?” It proves integrity, consistency, and provenance, so you are not just collecting identity details. Instead, you build confidence in the data over time and across sessions. This makes later decisions more reliable and easier to defend.
The Identity Verification Process with Digital Identity Solutions
The full identity verification process comes with many steps. When teams say they “verify identity,” results can vary a lot. That is, unless the identity verification process is clearly designed. Good digital identity solutions systems define what complete verification means for each industry, service, channel, and risk tier. They also set clear rules for how to handle errors, retries, and exceptions. A step-by-step process helps teams stay consistent as check volume and the level of fraud risk change.
To make this practical, the sections below show how comprehensive digital identity verification can be delivered using automated processes. They also explain where manual identity verification may still be used as a fallback. In most cases, manual verification should be limited to edge cases and high-risk scenarios. The goal is to keep the customer experience smooth while maintaining strong fraud protection.
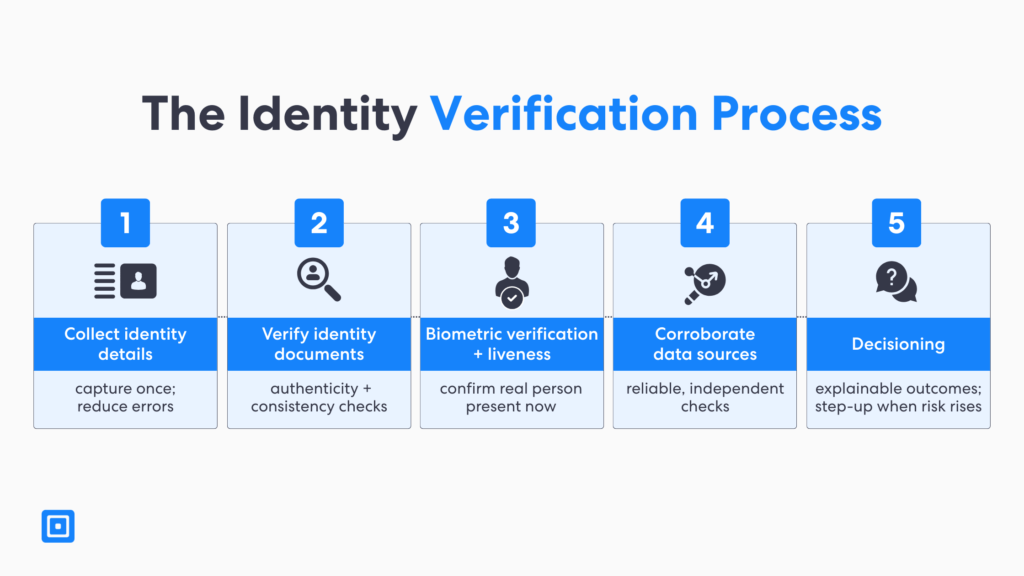
- Step 1: Collect identity details: Capture core identity data (name, DOB, address, contact details) and any required identifiers based on regulation and risk.
- Step 2: Verify identity documents: Check document authenticity and validity signals (security features, data consistency) to reduce identity theft and weak “knowledge” checks.
- Step 3: Biometric verification and liveness detection: Use facial recognition and liveness detection to confirm a real person, and protect biometric data with secure storage.
- Step 4: Corroborate against reliable data sources: Cross-check identity details with independent sources (e.g., registries, internal records, credit bureaus where permitted) to raise confidence.
- Step 5: Decisioning for complete verification: Produce explainable outcomes (pass, fail, step-up) with consistent rules aligned to fraud risk and audits.
Fraud Risk with Digital Identity Verification
Throughout this blog, it is clear that fraud risk is tied to digital identity verification. To illustrate how fraud risk works under pressure, it is essential to consider examining a common attack pattern. Typically, fraudsters begin with a low-friction flow. They check whether the same device has been previously blocked, and then retry with new identity documents or synthetic identities. Another method they may try is rotating a phone number or the user’s email address to bypass basic risk controls. This type of risk flow can result in fast, repeated attempts that simple rules may miss.
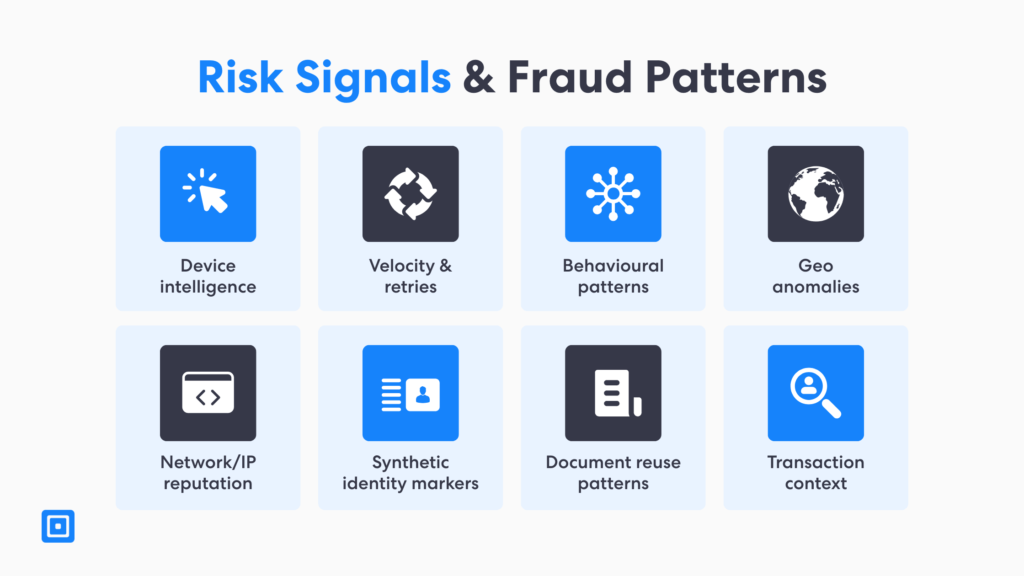
Due to this, ID verification solutions require artificial intelligence and machine learning to spot suspicious patterns across fraud risk attempts. It is verification tools like these that can flag unusual velocity of identity checks, repeated session failures, or any inconsistent identity information across sessions. The end goal is to protect the business and prevent fraud, not to punish genuine customers. When identification protocols and processes are well-tuned, it reduces manual verification and supports a smoother overall customer experience.
Traditional Methods and Manual Verification
Manual verification and traditional methods, such as knowledge-based security questions, were built for a different era of risk protection. Today, leaked data and large-scale automation make it easier for attackers and fraudsters to pass “what you know” checks. This is especially true when identity theft has already occurred and identity details are exposed. As a result, these verification approaches can increase fraud risk without improving overall security.
However, manual identity verification can still be helpful in rare edge cases. The issue is that it does not scale well. It often negative impacts the customer experience. Automated processes provide consistent results, faster decisions, and stronger audit trails. It helps teams apply the same identity verification process across channels and services. Manual verification review is best reserved for tightly defined, high-risk exceptions.
Frameworks for Digital Identity Solutions
Digital identity solutions require a strong framework. To operationalize digital identity validation, it is important to use a four-part model without adding unnecessary friction. This type of model keeps teams aligned across product, compliance, and security. It makes outcomes much easier to monitor and improve.
- Validate: Check document authenticity, tampering, and data consistency to reduce obvious fraud and manual verification.
- Corroborate: Confirm identity details using independent data sources (e.g., registries, internal records, credit bureaus where allowed).
- Defend: Use risk signals and behavioral analytics to spot synthetic identities, retries, and suspicious patterns with minimal friction.
- Decide: Apply explainable pass/step-up/decline rules and trigger MFA/2FA when risk is higher.
This four-part framework also cleanly maps out to different identity verification platforms. It separates evidence quality from final decision-making. Fine-tuning operational performance while keeping regulatory requirements in mind to keep fraud risk management intact.
Secure Data Storage and Privacy
Digital identity solutions are only as trustworthy as the way they handle their data storage and privacy. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) guidance emphasizes the importance of protecting sensitive data. Exposure can lead to more fraud, identity theft, and damage to long-term brand trust. Strong controls around secure data storage can reduce the risk of insider misuse and accidental data leaks. It is essential for protecting both customers and organizations.
In practice, secure storage and data privacy processes include multiple factors. They cover encryption, privilege access, retention limits, and disciplined vendor management. It is crucial to design workflows that minimize the amount of biometric data that you actually keep. This limits the potential damage if data breaches do occur. Regular audits and access reviews help keep controls effective over time. Clear incident plans also support a fast response when issues arise.
Authentication After Verification: MFA, 2FA, and Continuity
Authentication proves identity immediately after verification. It protects access from that moment onward. This is crucial, especially when the fraud risk shifts from the onboarding journey to account takeover. Multi-factor authentication and two-factor authentication can reduce that risk. This kind of layered approach helps prevent attackers even if they have stolen information or credentials.
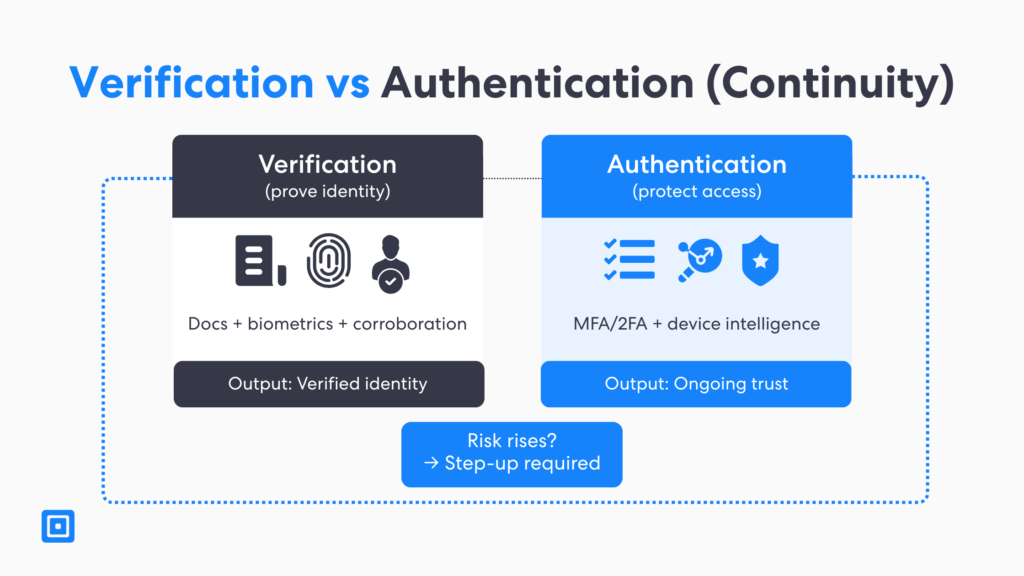
Imagine a verified user trying to access an account suddenly from a new mobile device. There are unusual login patterns present as well. This will prompt teams to step up verification pathways. This is a perfect example of how “same device” intelligence can help verify identities. Any additional factor authentication helps balance security and access with a much smoother customer experience.
Financial Institutions and Regulated Sectors
It is incredibly common for financial institutions and other regulated sectors to face strict Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations. There is close scrutiny of the quality of the identity verification process. Clear rules on accepted evidence, the exceptions that apply, and how monitoring works are necessary for any risk-based program. Consistent outcomes across various channels and online services are also needed. This clarity helps to reduce errors and improve audit readiness.
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) framework is widely referenced. It links identity verification and digital identity solutions to risk and governance. It supports an organized approach to choosing data sources, setting appropriate controls, and documenting decisions. Teams that align policy, controls, and monitoring lower overall fraud risk, all while maintaining a strong customer experience. It is also easier to adapt when threats and regulations change over time.
Case Study: Companies House Identity Verification Rollout (UK, Nov, 2025)
The UK sought to reduce misuse of company registrations for illegal purposes by strengthening identity assurance for people who set up, run, own, or control companies. This included addressing risks tied to fraud and identity manipulation and improving trust in corporate records.
Companies House Identity Verification Goes Live for Directors and PSCs
Companies House confirmed that legal requirements for directors and people with significant control (PSCs) to verify their identities would begin on 18 November 2025, using routes including gov.uk One Login and alternative channels for those who need them.
Outcomes
More than 1 million people verified early after the voluntary launch in April 2025, signalling strong uptake ahead of mandatory changes.
By a later milestone, more than 1.5 million people had verified since April 2025, supporting a staged shift toward stronger transparency and less identity abuse.
The gov.uk ID Checking App route averages under 2 minutes 30 seconds to complete, helping verification scale without heavy friction.
Choosing Identity Verification Solutions
It is essential to look for a comprehensive suite of identity verification products that support multiple evidence types and clear policy configurations. Ideally, choosing a tool that can be customized with building blocks based on your needs is a perfect fit. This is much better than forcing a one-size-fits-all workflow. It becomes significantly easier to pick controls that work for each service and separate risk tiers.
Other factors to consider when choosing digital identity solutions are secure data storage, audit trails, and explainability. Platforms that can show teams why a decision was made make it clear how to govern. It becomes easier to defend against regulatory requirements during audits or compliance reviews. That is why clear reporting reduces any additional manual verification work and speeds up investigations.
What Comprehensive Digital Identity Verifications Should Include
As mentioned before, comprehensive digital identity verifications include a combination of document authenticity checks, liveness detection, data source corroboration, and step-up authentication when risk arises. These additional layers verify identities with much stronger confidence. It also reduces the need for manual identity verification in routine cases. The result is a more consistent identity verification process.
Other products include monitoring of retries, fraud attempts, and performance by segment. This is a great demonstration of how companies can tune their automated processes to reduce any false rejects. This keeps fraud protection strong against fake identities and any evolving fraud patterns. Additional monitorinsyng helps you spot weak data verification sources or any broken user journeys early on.
Implementation Checklist for a Verification Program
An implementation checklist for any verification program begins with defining outcomes. Organizations need to determine what a “complete verification” means. Then, teams can map controls to each stage, covering identity documents, biometric data, device intelligence, behavioral analytics, and any authentication. Verifying consistently across channels and digital platforms becomes easier. It also makes roles and responsibilities clearer than ever across multiple teams.
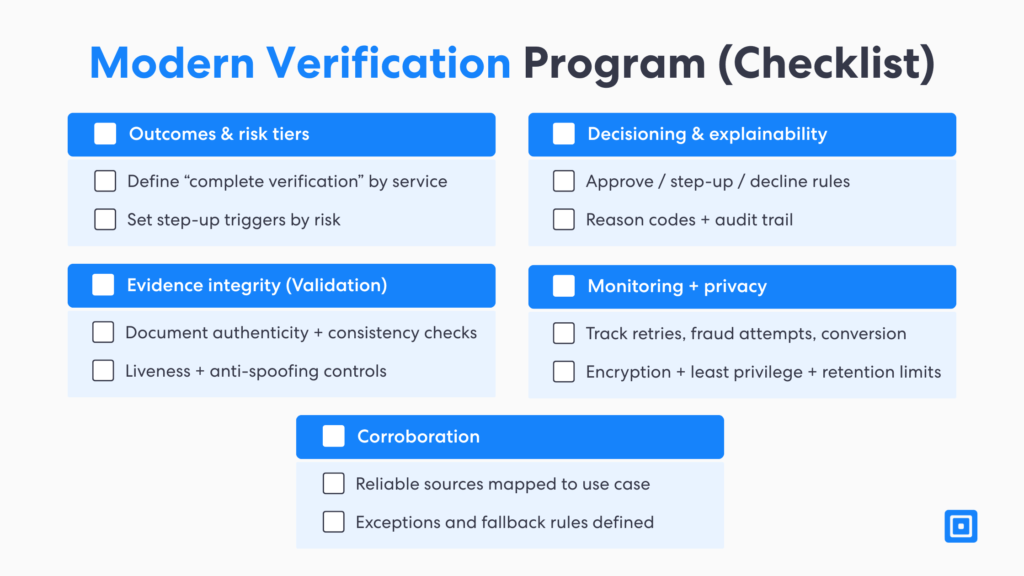
Feedback loops are built to become more efficient and improve over time. It is essential after major incidents or shifts in attack patterns to keep track of any fraud risk, conversion rates, retries, exception reasons, and review controls. Companies can ensure that their identity verification processes are aligned with business growth and changing customer expectations. This helps reduce any false declines without seriously weakening fraud protection.
Key Takeaways
Digital identity solutions work best when digital identity validation is an integrity layer.
A digital identity check should be clear, policy-led, and based on risk signals.
Secure data storage and privacy by design reduce damage from data breaches.
Strong programs scale automated processes and limit manual identity verification to rare cases.
Comprehensive digital identity verification combines documents, biometrics and data sources.
ComplyCube’s Digital Identity Solutions
If your goal is to verify identity, reduce identity theft, and improve customer experience across digital platforms, the strongest approach is validation-first: prove the integrity of identity data, corroborate it with reliable sources, defend against fraud patterns, and decide with clear policy logic. ComplyCube helps businesses implement digital identity solutions that support fast, secure verification journeys so you can protect access, meet regulatory requirements, and keep genuine customers moving. Connect with our team today.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do digital identity solutions reduce fraud without slowing down online onboarding?
Digital identity solutions combine identity documents, biometric verification, and trusted data sources to verify identity quickly while keeping controls strong. They use risk signals to apply step-up checks only when needed, so genuine customers are not forced through heavy friction.
What should a strong digital identity verification process include from end to end?
A strong identity verification process typically follows five steps: collect identity details, verify identity documents, run biometric verification with liveness detection, corroborate against reliable data sources, and apply explainable decisioning. Each stage should have clear rules and measurable outcomes, so “complete verification” is consistent across services and risk tiers.
What is the practical difference between a digital identity check and digital identity validation?
A digital identity check is the real-time decision point that determines whether a user should get access, based on evidence and fraud risk. Digital identity validation is the deeper integrity layer that proves identity data and evidence are trustworthy, consistent, and defensible across sessions.
How can businesses use risk signals and behavioral analytics to spot synthetic identities early?
Risk signals such as rapid retries, unusual navigation patterns, and inconsistent identity details can indicate synthetic identities or scripted attacks. Behavioral analytics and machine learning help detect these patterns across attempts faster than manual verification, especially at scale.
How can ComplyCube help teams implement validation-first digital identity solutions at scale?
ComplyCube helps businesses implement digital identity solutions with policy-led decisioning, strong identity document checks, biometric verification, and corroboration across trusted data sources. A validation-first approach improves confidence in identity data, reduces false declines, and limits manual verification to high-risk exceptions.