TL;DR: Social security number validator tools are essential in verifying customer identity. Leveraging KYC social security validation can help organizations meet regulatory requirements faster. AML social security validation enables risk-based due diligence, helping organizations flag risky profiles early in the customer life cycle.
What are Social Security Number Validators?
Social Security Number (SSN) validators are tools or systems that verify current SSNs. They check if numbers are valid, formatted correctly, and historically consistent with official insurance data. Validator tools also review details such as the structure of the SSN, its issuance location and timeframe. They run information against taxpayer identification numbers or lists of known invalid numbers or those associated with deceased individuals.
Particularly, SSN validation is a foundational process for financial institutions, government agencies, and other regulated entities. They confirm identities in order to prevent the misuse of social security benefits and prevent financial crime. The SSN functions as a unique identifier for U.S. citizens, permanent residents, and certain non-resident aliens. Proper validation helps ensure that each number truly belongs to the individual claiming it.
Therefore, using SSN validators supports compliance with KYC regulation standards and helps protect against identity theft. It prevents fraud and unauthorized access to sensitive data. By confirming that an SSN is authentic and accurately linked to the right person, institutions can strengthen fraud prevention. It can help protect customer information and guarantee that benefits or transactions are granted only to eligible individuals.
How Customer Identification Programs Depend on SSN Verification
Modern customer identification programs are designed to verify a customer’s identity as part of the Know Your Customer (KYC) process. Organizations must ensure that the user identity is real. Organizations must ensure that the user identity is real, correct, not linked to synthetic identities, identity theft, or fraudulent transactions.
Social security number validators focus on matching identity documents to SSNs. They do this with driver’s licenses and other forms of government-issued identification to ensure that the SSN belongs to the correct individual. This helps companies and organizations establish user or customer authenticity and comply with legal requirements.
As a result, CIPs must include procedures for responding to situations where a bank cannot verify a customer’s identity. They must also include record-keeping and retention requirements for customer identification information. Additionally, financial institutions are required to conduct continuous monitoring of customers as part of their compliance efforts. You can learn more here: Customer Identification Program: What Is CIP?
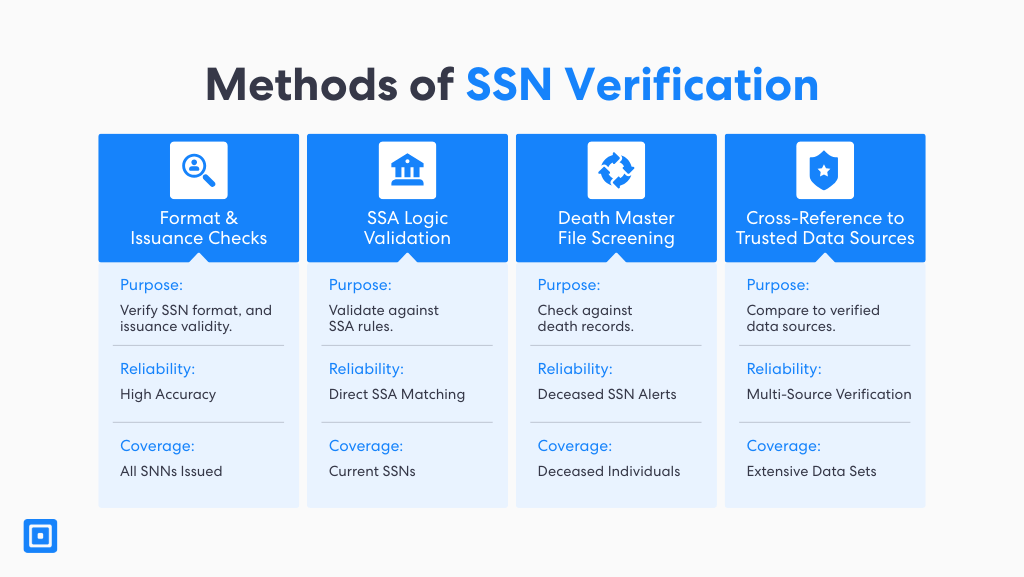
Methods of SSN Verification
Regulated entities and other financial institutions have access to several methods for SSN verification. Each offers signals that contribute to a broader identity verification framework. For instance, when used in combination, these techniques form a layered verification process that goes beyond confirming SSN validity. It helps institutions determine whether a security number is genuinely tied to the customer’s identity.
Moreover, this approach supports compliance with the USA Patriot Act, the Bank Secrecy Act, and additional guidance from the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN). It also enables stronger risk assessment, fraud prevention, enhances security, and provides more accurate customer verification outcomes across regulated industries.
Format and Issuance Checks
Firstly, SSN validation examines structural and historical correctness. The format can confirm whether an SSN follows the correct nine-digit pattern. It ensures that numbers fall within known issuance ranges based on geography and issuance date. Assessing these formatting details can flag obviously invalid SSNs before requiring even deeper levels of verification.
SSA Logic Validation
Then, the next step is using logic validation to test against official rules set by the Social Security Administration (SSA). This includes confirming whether the number was ever issued, whether it has been marked as restricted, and whether it aligns with the customer’s personal details, such as the name and date of birth. In automated workflows, logic checks result in higher data accuracy and improved outcomes during compliance reviews.
Death Master File Screening
Similarly, to guard against identity theft involving deceased individuals, many institutions screen SSNs against the SSA Death Master File (DMF). This database contains information on individuals reported as deceased and is a key control for detecting invalid or fraudulently used SSNs. Screening against the DMF ensures that the SSN provided is not associated with a deceased person. Incorporating this step into customer identification programs enhances trust and reduces compliance risks associated with onboarding fake or inactive profiles.
Cross-Reference to Trusted Data Sources
Finally, cross-referencing SSNs against trusted data sources such as credit bureaus, utility records, and proprietary databases provides an additional layer of validation. These systems verify whether an SSN is correctly linked to consistent name, address, and date-of-birth records across institutions. Modern platforms may use AI-driven fraud detection and automated verification to assess behavioral patterns and flag inconsistencies in SSN usage.
By combining these four methods, financial institutions can meet the stringent requirements of AML regulations. It can help prevent fraud, improve onboarding integrity, and prevent crime and suspicious patterns at the point of customer interaction. This layered approach helps ensure regulatory compliance with business transactions, improves data accuracy, and delivers a more secure and frictionless experience for customers navigating KYC processes in an increasingly digital world.
SSN Data Accuracy and Customer Information Verification
When SSN records are clean and current, risk models tend to perform better. This allows investigations to focus on the highest-risk cases. Poor data accuracy only increases the risk of onboarding fake profiles. Missing key red flags in risk assessment workflows is absolutely necessary. Accurate SSN data ensures alignment with official records from the Social Security Administration and helps avoid additional compliance risks.
In addition to confirming identity, high-quality SSN data helps institutions avoid onboarding fake profiles. Through verification, organizations can now better prevent identity fraud, false claims, and synthetic identities. With growing threats, verifying customer information with a social security number validator supports early detection. It also prevents escalation into full-scale financial crime investigations.
How Social Security Number Validators Aid AML Compliance
Effective AML compliance begins with rigorous identity verification. Financial institutions, fintech platforms, and other regulated entities must ensure that every customer or business partner is accurately identified before granting access to products or services. SSN validation plays a vital role in this process. In AML programs, social security number validators help detect synthetic identities, inconsistencies across records, and unusual profile changes. These markers may often indicate money laundering risk.
However, by validating against trusted government sources, such as the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and the Social Security Administration (SSA), institutions can strengthen their regulatory compliance stance. This can also reduce exposure to fraudulent activity. These SSN checks flag suspicious activity early in the onboarding process. These are key requirements under the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and other similar AML regulations.
Therefore, AML-focused SSN validation ensures that firms operating across multiple jurisdictions can satisfy both domestic and international legal obligations efficiently. The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) and other supervisory authorities demonstrate a proactive commitment to risk management, transparency, and data integrity. Ultimately, integrating SSN validation into a broader AML framework enhances due diligence, supports customer trust, and reinforces compliance readiness in an increasingly complex regulatory landscape.
Case Study: U.S Bank Uses Social Security Number Validator to Enhance Due Diligence
U.S. Bank faced a rising number of synthetic identities entering its digital onboarding process. Without real-time SSN verification, the bank suffered from manual errors, delayed escalations, and inconsistent outcomes across regional teams.
Implementing Social Security Number Validators
As a result, the bank used a social security number validator with its KYC processes and biometric verification system. SSNs were checked instantly for validity, duplication, and linkage to high-risk profiles or other regulated entities. Then, this triggered additional verification where needed.
Outcomes
38% reduction in fraud attempts using synthetic or invalid SSNs
22% improvement in customer verification time for digital applications
Significant increase in regulatory reporting accuracy and wage reporting integrity
Fraud Prevention Through Additional Verification Layers
Fraud prevention doesn’t stop at validating a single data point. Forward-thinking institutions now employ layered verification checks that combine multiple signals to build a complete picture of a customer’s identity. These elements work together to confirm that the individual’s Social Security Number (SSN) is valid, current, and legitimately associated with the person submitting it. Cross-referencing this data through background checks and trusted databases strengthens the accuracy and reliability of identity verification.
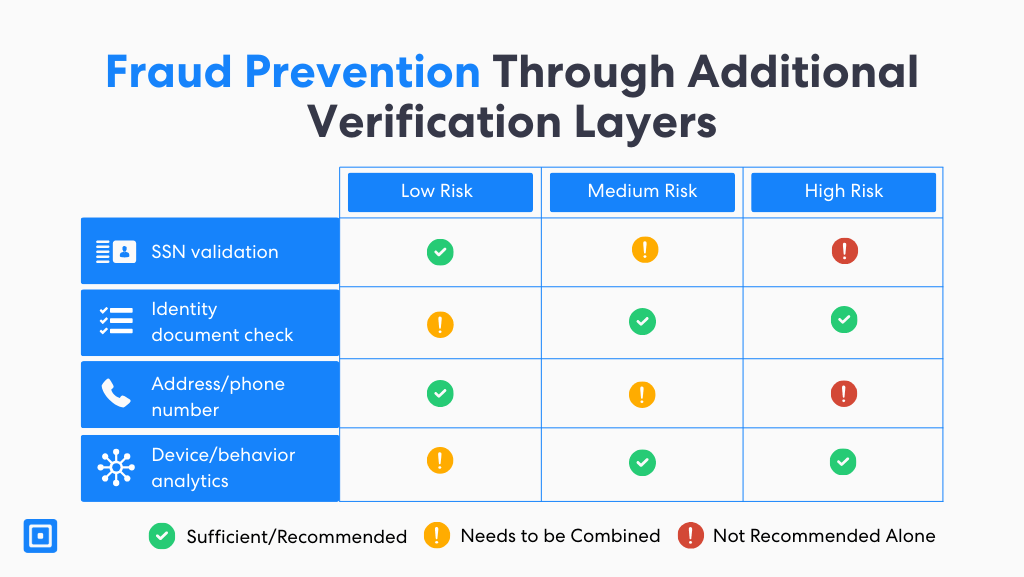
When an SSN or associated data point triggers a potential risk indicator, enhanced due diligence (EDD) workflows are activated. It examines the broader customer profile in greater detail. This multi-layered approach helps institutions uphold Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) requirements.
In general, multi-layered approaches actively protect against terrorist financing and reduce exposure to criminal activities across linked fraud networks. By integrating these verification safeguards, organizations can detect anomalies earlier, prevent systemic risks, and maintain trust and compliance in an increasingly complex regulatory landscape.
Ensuring Compliance with Changing AML Regulations
Ensuring compliance means using tools such as a social security number validator to keep up with changing AML regulations. To remain audit-ready, firms must show proactive control over their verification stack. Having an up-to-date verification stack only enables faster updates to rules as regulations evolve.
Consequently, changing AML regulations apply to other regulated industries beyond banking. It covers fields such as real estate, crypto, and lending. AML regulations typically come into play where there is frequent onboarding of new customers. This is important as most of the time, there isn’t adequate identity verification, which opens the door to money laundering and other financial crimes.
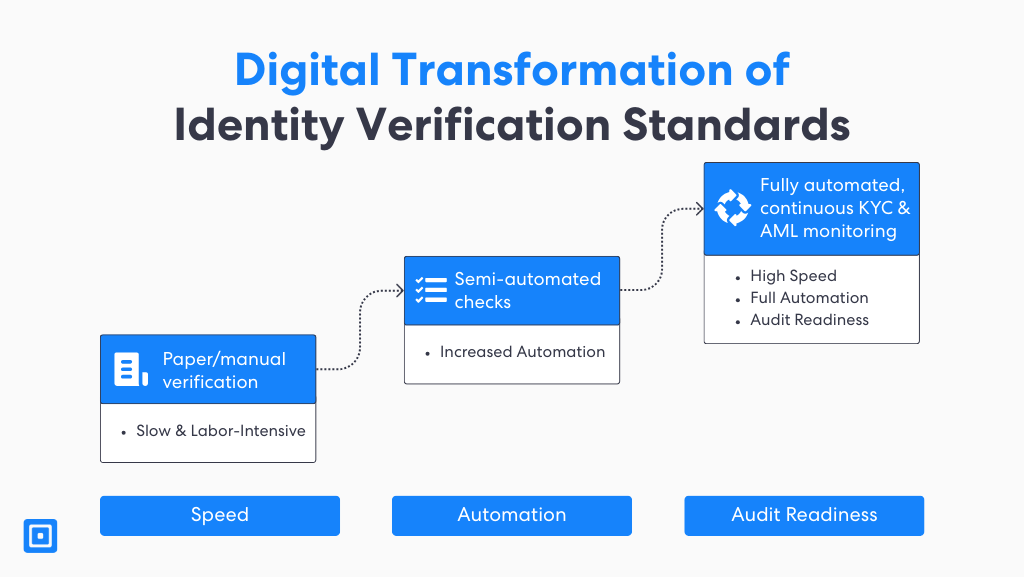
Digital Transformation of Identity Verification Standards
The rapid shift to online services has amplified the need for identity verification. Firms must ensure that this process is both thorough and frictionless. As customers expect seamless digital experiences, regulated institutions must balance convenience with security. They must ensure that compliance standards are never compromised.
In fact, technologies such as automated identity verification, AI-driven risk scoring, and digital document analysis are now central to this effort. It enables organizations to detect anomalies and validate identities efficiently at scale.
Within this evolving ecosystem, a Social Security Number (SSN) validator plays a critical role. SSN validation enables real-time identity checks, verifies data against trusted sources, and supports omni-channel onboarding flows with minimal user friction.
When integrated into broader compliance frameworks, SSN validation enhances data accuracy, improves risk modeling, and streamlines regulatory reporting. Ultimately, it helps institutions manage digital transformation responsibly. It is important to maintain compliance integrity while delivering seamless experiences that today’s users demand.
Blockchain Technology and Future-Proof Identity Validation
Emerging technologies such as blockchain are introducing possibilities for creating secure, verifiable, and privacy-preserving digital identities. Institutions can issue credentials that are tamper-resistant and cryptographically authenticated, reducing reliance on centralized databases. When combined with artificial intelligence, these innovations pave the way for decentralized identity verification.
Furthermore, future-proofing identity verification allows organizations to perform real-time risk assessments without unnecessarily exposing sensitive personal identifiers. This approach aligns closely with global data privacy principles, improving both security and transparency across verification ecosystems. Despite these advancements, foundational identifiers such as the Social Security Number (SSN) remain critical for linking customers to existing financial and governmental systems.
So, until decentralized identity infrastructure achieves full interoperability, thorough SSN validation continues to serve as a cornerstone of compliance and trust. Integrating SSN checks with electronic verification methods ensures data accuracy, supports regulatory reporting, and helps institutions. It manages the transition between traditional and emerging identity frameworks safely and effectively.
Key Takeaways
Social security number validators enhance trust and reduce fraud during onboarding.
KYC social security validation is a regulatory expectation in the U.S.
AML social security validation detects suspicious identity patterns.
Third-party SSN validation avoids reliance on direct government APIs.
ComplyCube integrates SSN checks through social security number validators into a layered identity workflow.
ComplyCube’s Social Security Number Validator
To summarize, ComplyCube provides compliance trusted by regulated entities globally. It supports ID verification, customer analysis, and data validation using SSN verification programs. Stacking this on top of existing processes allows teams to meet KYC and AML compliance obligations. Ultimately, whether it be a bank, lender, or crypto firm, ComplyCube enables teams to prevent financial crime and reduce false positives, all in a single no-code workflow.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a social security number validator and why is it important?
A social security number validator is a tool that confirms whether a person’s SSN is valid, correctly formatted, and associated with their identity. It’s critical for verifying current or former employees, business directors, new users, etc.
How does SSN verification help with identity theft prevention?
By confirming that SSNs are not stolen, reused, or synthetic, SSN verification helps detect early signs of identity theft. It also supports accurate risk scoring and can trigger escalations in KYC processes, helping organizations stay compliant with data privacy laws on handling sensitive data.
Is SSN validation enough for AML compliance?
Validation is not enough on its own. AML compliance requires many data checkpoints, including document and biometric checks. However, SSN validation is a foundational step in building customer identification programs that satisfy U.S. legal and data privacy requirements.
What are common challenges in verifying social security numbers?
Today, the most common challenges in verifying social security numbers are outdated internal systems, manual errors, lack of access to official records, and inconsistent integration with other tools. Third-party electronic verification systems solve these gaps with real-time automation. They do this while maintaining compliance with relevant data privacy laws.
How does ComplyCube ensure AML and KYC compliance using SSN checks?
ComplyCube incorporates social security number validator technology within a no-code platform that ensures data accuracy, biometric authentication, and regulatory compliance. We help financial institutions scale securely while upholding AML standards and protecting customer data privacy.