Compliance with financial crime regulations is crucial for every company. As part of this compliance, it’s essential to understand the definition of a Politically Exposed Person (PEP) to identify them and conduct additional due diligence as required by PEP KYC & Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws. Politically Exposed Persons can carry a level of risk for organisation, and therefore must be identified.
What is a Politically Exposed Person?
A politically exposed person is an individual who holds a prominent public function, such as a government official, high-ranking military officer, or senior executive in a major state-owned enterprise. A PEP generally presents a higher risk for potential involvement in bribery or corruption through their position and influence. Close business partners or family members of PEPs are often considered connected PEPs as they could pose an AML risk as well. Close associates of PEPs are also treated similarly due to the potential for influence and corruption, necessitating appropriate measures to manage these risks.
Definition and Meaning
A Politically Exposed Person (PEP) is an individual who holds a prominent public position or function, either domestically or internationally. This can include government officials, military officers, judges, senior executives of state-owned enterprises, and high-ranking officials of international organizations. PEPs are considered high-risk due to their potential influence and access to sensitive information, making them vulnerable to corruption, bribery, and money laundering. Identifying a politically exposed person (PEP) is crucial for financial institutions to mitigate the risk of financial crimes and ensure compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations.
Types of Politically Exposed Persons
There are several types of PEPs, including:
- Domestic PEPs: These individuals hold prominent public positions within their own country. Examples include government officials, high-ranking military officers, and judges. Their influence and access to national resources make them susceptible to corruption and bribery.
- Foreign PEPs: These individuals hold prominent public positions in other countries. This category includes heads of state, government ministers, and senior government executives. Due to their international influence, they pose a significant risk for cross-border money laundering activities.
- International Organization PEPs: These are individuals who hold high-ranking positions in international organizations, such as the United Nations, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund. Their global reach and decision-making power make them potential targets for corruption and financial crimes.
- Immediate Family Members: Due to their close relationship with the individual, spouses, children, parents, and siblings of PEPs are also considered PEPs. Their association with a PEP can expose them to similar risks of involvement in illicit activities.
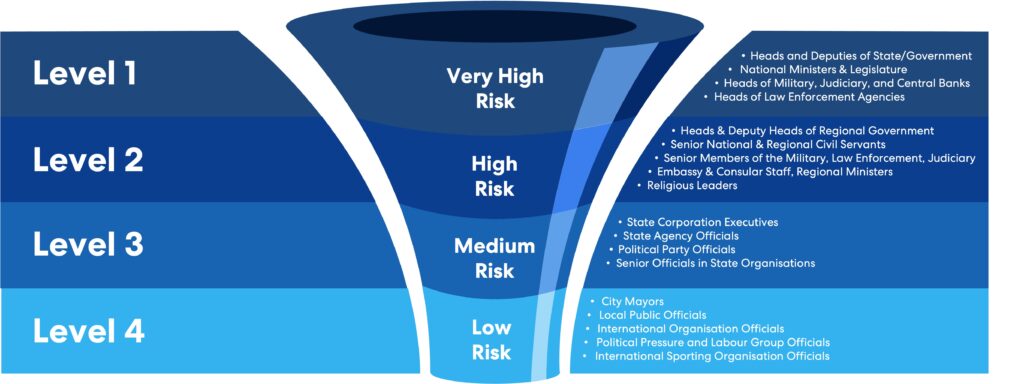
Levels of Politically Exposed Persons
PEP levels refer to the categorization of Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) based on the level of risk they pose in terms of potential involvement in bribery or corruption through their position and influence. PEPs can be broadly classified into four levels:
Level 1: Prominent figures representing an international body.
Level 2: Individuals holding a position at the national level.
Level 3: Officials holding a position at the state level.
Level 4: Civil servants holding a position at the local level.
Financial institutions are required to screen for PEPs and implement adequate AML measures based on these four levels to reduce their risks and liabilities. These measures are crucial to mitigate risk and manage potential risks associated with PEPs, ensuring compliance with money laundering and terrorist financing regulations.
Why is it Important to Conduct a PEP Screening?
All individuals meeting the definition of a PEP should be classified according to their risk level and screened before commencing a business relationship. Financial institutions must implement adequate PEP AML measures to reduce AML risks and liabilities. Effective customer identification is crucial in PEP screening to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and mitigate risks associated with high-risk customers.
Increased scrutiny from local and international financial regulatory authorities makes it crucial for financial institutions to protect themselves from fraud and financial crimes. Fines imposed by bodies like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) for non-compliance with AML laws and regulations have reached millions of dollars, providing a strong motivation for businesses to screen for PEPs. Understanding the risk profiles of each customer or beneficial owner is essential in managing potential money laundering and terrorist financing risks. That’s why many financial institutions often assume the “once a PEP, always a PEP” approach (ongoing PEP status), even when clients abandon their governmental or civic positions.
PEP (Politically Exposed Person) screening is crucial for businesses as it helps mitigate the risks associated with financial crimes
Andreea Balasa, Growth Manager at ComplyCube, states, “PEP (Politically Exposed Person) screening is crucial for businesses as it helps mitigate the risks associated with financial crimes, corruption, and money laundering. By identifying and monitoring high-risk individuals, companies protect their reputation, ensure compliance with regulatory standards, and maintain trust with stakeholders and customers.”
How to Conduct PEP Due Diligence
PEP due diligence is conducted based on the level of risk that each Politically Exposed Person (PEP) presents. Level 1 PEPs include those representing international bodies, while level 2 PEPs are individuals holding a position at the national level. Level 3 PEPs are officials holding a position at the state level, and level 4 PEPs are civil servants holding a position at the local level. The risk level associated with each PEP determines the extent of the due diligence required, with higher-risk PEPs requiring more thorough due diligence. Understanding the unique characteristics of each customer relationship is crucial in determining the appropriate level of due diligence.
It’s important to note that the specific due diligence steps and risk assessment may vary based on the jurisdiction and regulatory requirements. Financial institutions must develop risk-based policies and procedures for the PEP due diligence process to comply with AML laws and regulations. Accurately identifying politically exposed persons is essential, as outdated or incomplete public sources can pose challenges, making advanced electronic platforms vital for efficient and accurate PEP screening.
Generally speaking, PEP due diligence should incorporate the following aspects:
- Employ a Risk-Based Approach: The risk-based strategy provides a complete picture of a company’s high-risk customers and those situations that warrant high-risk status.
- Obtain Additional Identifying Information: Provide a questionnaire to high-risk clients tailored to the risk-based policies to gain in-depth customer knowledge and the risks they may pose.
- Analyze the Source of Funds: Under the EU’s Fourth Money Laundering Directive (MLD4), legal organizations are expected to hold up-to-date Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO) records in a register open to authorities and other persons of genuine interest.
- Ongoing Transactions Monitoring: Obtain transaction details, such as history, purpose, and nature, and analyze information, such as the duration of the transaction and the parties involved.
- Adverse Media Check: To build a complete customer KYC profile of your client and their reputation, you must thoroughly review related press articles and analyze relevant information. The overwhelmingly negative results strongly indicate that they are too risky for business. If the results are positive, businesses should take the following due diligence step.
- Draft Your Report for Further Review: Compile your due diligence report for internal and future regulatory reviews before onboarding.
- Develop an Ongoing Risk-Based Monitoring Strategy: Continuous high-risk client monitoring is time-consuming and requires much effort, so using a risk-based monitoring strategy is optimal.
Data Sources for PEP Identification
Financial institutions and other organizations can use various data sources to identify PEPs, ensuring they take appropriate measures to mitigate associated risks. These sources include:
Government Lists: Official lists of government officials, politicians, and other public figures provide a reliable source of information for identifying PEPs.
Publicly Available Information: News articles, social media, and other publicly available sources offer valuable insights into individuals’ public roles and affiliations, helping to identify PEPs.
Commercial Databases: Specialized databases compile information on PEPs, including their names, positions, and affiliations. These databases are essential tools for financial institutions to conduct thorough PEP screening.
Sanctions Lists: Lists of individuals and entities subject to economic sanctions often include PEPs. These lists help financial institutions identify high-risk individuals and entities that require enhanced due diligence.
- Adverse Media: Reports of negative news or adverse information about an individual or entity can indicate a higher risk of money laundering or other illicit activities. Monitoring adverse media helps financial institutions stay informed about potential risks associated with PEPs.
By utilizing these data sources, financial institutions can effectively identify PEPs and implement measures such as enhanced due diligence and ongoing monitoring to mitigate the risks associated with them. This proactive approach helps protect against financial crimes and ensures compliance with AML regulations.
Fortify Your AML Controls
To sum up, understanding the definition of a PEP and the importance of conducting due diligence on them is critical for financial institutions to comply with AML laws and regulations. With increased scrutiny from regulatory authorities, financial institutions must implement adequate measures to reduce their risks and liabilities. By following a risk-based approach and conducting thorough due diligence, businesses can protect themselves from financial crimes and potential fines.
ComplyCube provides comprehensive AML compliance solutions, including PEP screening, to help businesses mitigate risks and ensure compliance. Contact us to learn more about our services and how we can help you safeguard your business against financial crimes.