While traditionally viewed as less exposed than banks, insurance companies, particularly those offering life insurance, annuities, and investment-linked products, have increasingly found themselves under scrutiny from regulators. Identifying and monitoring suspicious activities is a critical component of AML efforts in this sector. Insurance companies are classified as financial institutions under the Bank Secrecy Act and must implement specific compliance measures, including filing suspicious activity reports, to satisfy regulations set forth by authorities like FinCEN. For any insurance firm, a well-structured Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance program is no longer just a regulatory obligation; it is a strategic imperative to safeguard the integrity of their operations and maintain trust with policyholders, regulators, and investors. This guide will break down key AML guidelines for insurance companies to prevent fraud and ensure compliance.
Introduction to Anti Money Laundering
Anti-money Laundering (AML) refers to the comprehensive set of laws, regulations, and procedures designed to prevent and detect the laundering of illicit funds. In the insurance sector, AML is crucial to prevent the exploitation of insurance products and transactions for money laundering purposes. Insurance companies must implement robust AML measures to identify and report suspicious transactions, verify customer identities, and monitor transactions to prevent the flow of illicit funds.
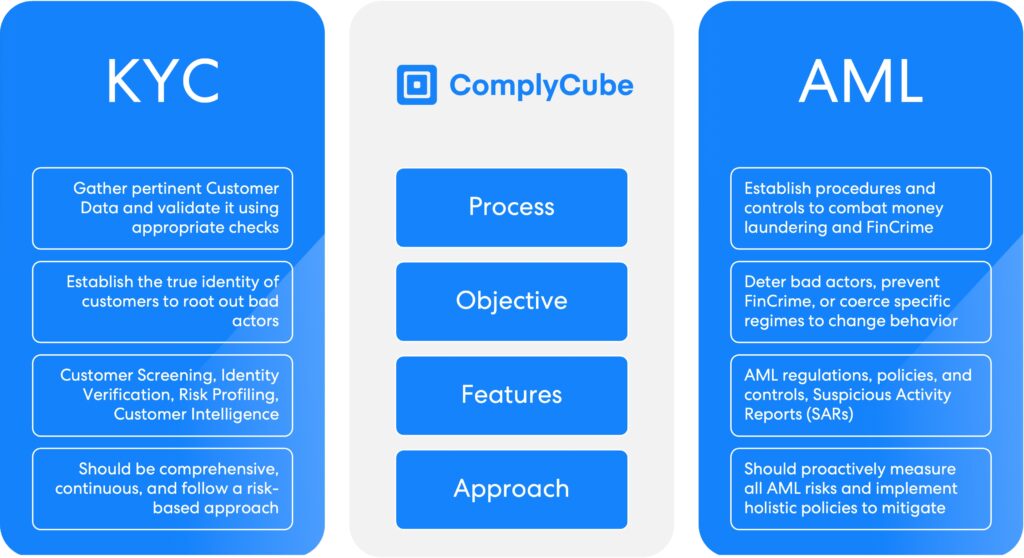
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) provides essential guidance on AML regulations, and insurance companies must adhere to these regulations to avoid severe penalties and reputational damage. By embedding AML practices into their operations, insurance firms can safeguard their integrity and contribute to the global fight against financial crime.
AML Risks Faced By Insurance Firms
Insurance products can present unique vulnerabilities when it comes to financial crime due to various risk factors such as the complexity of products and the involvement of multiple parties. For example, policies with investment components can be used to obscure the origin of illicit funds, while early withdrawals and beneficiary changes may serve as red flags for laundering or fraudulent activity.
Criminals often exploit insurance products to transfer large sums of illicit funds, particularly through single premium policies and top-ups. The use of third parties, such as brokers or agents, further complicates oversight and weakens direct visibility into the customer relationship.
Money launderers often favor insurance products because they offer perceived stability, large transaction values, and, in some cases, reduced scrutiny compared to traditional banking. As a result, insurance firms are expected to demonstrate the same level of AML diligence as other financial institutions, as they face av very real risk of fraud.
Navigating Regulatory Expectations
Insurance companies operate under a complex patchwork of international and domestic AML regulations. At a global level, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) provides a comprehensive set of recommendations that shape national legislation. In Europe, the EU’s Anti-Money Laundering Directives (AMLD) impose stringent obligations, including Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for high-risk customers and beneficial ownership transparency. In the United States, the Bank Secrecy Act and the USA PATRIOT Act outline detailed AML program requirements for insurers. Similarly, most European nations have similar regulatory bodies governing AML practices, such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK, or Germany’s BaFin. These regulatory bodies apply sector-specific guidance and actively enforce compliance. Non-compliance with these AML regulations can result in serious consequences, including hefty fines and other penalties.
To remain compliant across jurisdictions, insurance companies must align their AML programs with both global standards and national expectations. This is a task that demands flexibility, precision, and often the support of advanced technology.
The Building Blocks of Anti Money Laundering Compliance in Insurance
At the core of any effective AML framework lies the risk-based approach. Rather than applying uniform procedures across all customers and products, insurers must tailor their compliance controls to match the level of risk presented. This requires ongoing risk assessments that consider factors such as product type, customer profile, delivery channels, and geographic exposure. Identifying and reporting suspicious activities is crucial in this context to ensure compliance and prevent financial crimes.
Higher-risk customers may require additional verification procedures.
“The Know Your Customer risk-based approach enables a better customer onboarding compliance program by adjusting verification levels based on risk factors. Low-risk customers are accepted more quickly, whereas higher-risk customers may require additional verification procedures,” shares Financial Crime Academy. For more information on the risk-based approach, read “The Evolution on the Risk Based Approach in AML.”
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is a foundational pillar of AML. Before issuing a policy, insurance companies must verify the identity of the customer and, where applicable, the beneficial owner. For standard-risk individuals, basic checks may suffice, but for Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs), clients from high-risk countries, or those with unusual transaction behavior, Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is necessary. This includes obtaining additional documentation, understanding the source of funds, and conducting more frequent reviews. For more on CDD, read “What is Customer Due Diligence?”

However, identity verification must not stop at the onboarding stage. Ongoing monitoring is critical to detect unusual activity over the life of a policy. For example, unusually large premium payments, sudden changes to a policy’s beneficiaries, or frequent early surrenders could indicate an attempt to launder funds. To detect such patterns, insurance companies are increasingly turning to AI-powered monitoring tools capable of analyzing large volumes of data and identifying subtle anomalies that might be missed in a manual review.
“We’ve seen a worrying rise in insurance fraud made possible by identity theft. Stolen personal information can be used for every financial crime imaginable, and victims of impersonation who are often elderly or vulnerable, face devastating consequences.“
Ursula Jallow, Director at the Insurance Fraud Bureau states, “We’ve seen a worrying rise in insurance fraud made possible by identity theft. Stolen personal information can be used for every financial crime imaginable, and victims of impersonation who are often elderly or vulnerable, face devastating consequences.“ This underlines why businesses must implement advanced biometric technology to prevent cases of identity fraud and safeguard their operations.
Insurance Products and Money Laundering
Insurance products, particularly those with a cash value such as life insurance and annuities, can be vulnerable to money laundering. Money launderers may exploit these products to launder illicit funds by overpaying premiums, surrendering policies prematurely, or making fictitious claims.
Insurance companies must be vigilant about these risks and implement stringent measures to prevent them, including rigorous transaction monitoring and thorough verification of customer identities. The insurance industry is also susceptible to premium fraud, where policyholders exaggerate or fabricate claims to receive payouts. To combat these threats, insurance companies must implement robust controls to ensure that their products are not used for money laundering purposes and to maintain compliance with AML regulations.
AML Red Flags To Identify
Identifying red flags for money laundering is crucial for insurance companies to prevent financial crime. Common red flags include suspicious transactions such as large cash payments or payments from unrelated third parties.
Other indicators include frequent changes in beneficiaries or covered assets, unusual payment methods, and policies with high cash values. Insurance companies must be vigilant in recognizing these red flags and report any suspicious activity to regulatory authorities.
The insurance industry is also at risk from shell companies and other illicit entities that may use insurance products to launder money. By diligently monitoring transactions and verifying customer identities, insurance companies can prevent the exploitation of their products for money laundering purposes and ensure compliance with AML regulations.
Implementing Cutting-Edge Technology
Outdated systems remain a challenge for many insurance firms, making it difficult to integrate real-time transaction monitoring or advanced analytics. However, modern RegTech solutions are increasingly accessible and scalable.
These platforms support automated onboarding, biometric identity verification, liveness detection, transaction screening, and real-time risk scoring. By adopting such tools, insurers can modernize their compliance posture while improving the customer experience, particularly important in a digital-first world where long onboarding processes can result in lost business.

Furthermore, many regulatory frameworks now encourage the use of technological solutions to meet compliance obligations more efficiently. Integrating these tools into existing operations allows insurance companies to shift from a reactive compliance model to a proactive, intelligence-led one.
Follow the Latest AML Guidelines for Insurance Companies Today
AML compliance is no longer a back-office function or a one-time effort at onboarding. For insurance companies, it is an ongoing, strategic process that touches every part of the organization—from underwriting to claims to customer service. In an environment where regulatory expectations are rising and criminals are constantly evolving, insurance companies that take a proactive, technology-driven approach to AML will be best positioned to mitigate risk, maintain trust, and grow responsibly.
For more information on how to fortify your business with cutting-edge KYC and AML, get in touch with our expert compliance team.