Preventing financial crime now demands the same speed and efficiency used to commit it. This is why a strong Know Your Customer Process (KYC) is crucial for every legitimate business, especially financial institutions where money laundering and other financial crimes are common.
But what exactly is KYC, and how can companies remain one step ahead of regulations while successfully satisfying evolving customer needs? This guide will break down the essential steps of KYC. It will explore the challenges of implementing KYC processes and discuss future compliance trends. By understanding these concepts, firms can design a KYC compliance strategy that is both effective and future-proof for long-term success.
The History of Know Your Customer (KYC) Processes
KYC obligations did not always exist. In fact, the KYC process has changed significantly over time through different legislation and jurisdictions. Its origins, however, are closely tied to efforts aimed at fighting money laundering, identity theft, and illegal financial activities.
The Early Drivers of KYC, Establishing Global Security
Financial crime worsened in the 1970s and 1980s, causing significant negative implications for many countries. Because of this, stronger KYC requirements were mutually recognized worldwide. The idea of KYC was formalized in the 1970s when the United States’ passed the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) in 1970. This law required financial institutions and banks to detect and report suspicious activities. The main goal was to fight money laundering and terrorist financing.
The Emergence of International Collaboration and Standards
In the 1980s, the rise of globalization made it easier for rapid financial transactions across borders. This contributed to loopholes in the financial systems that enabled criminals to commit financial crimes in different countries.
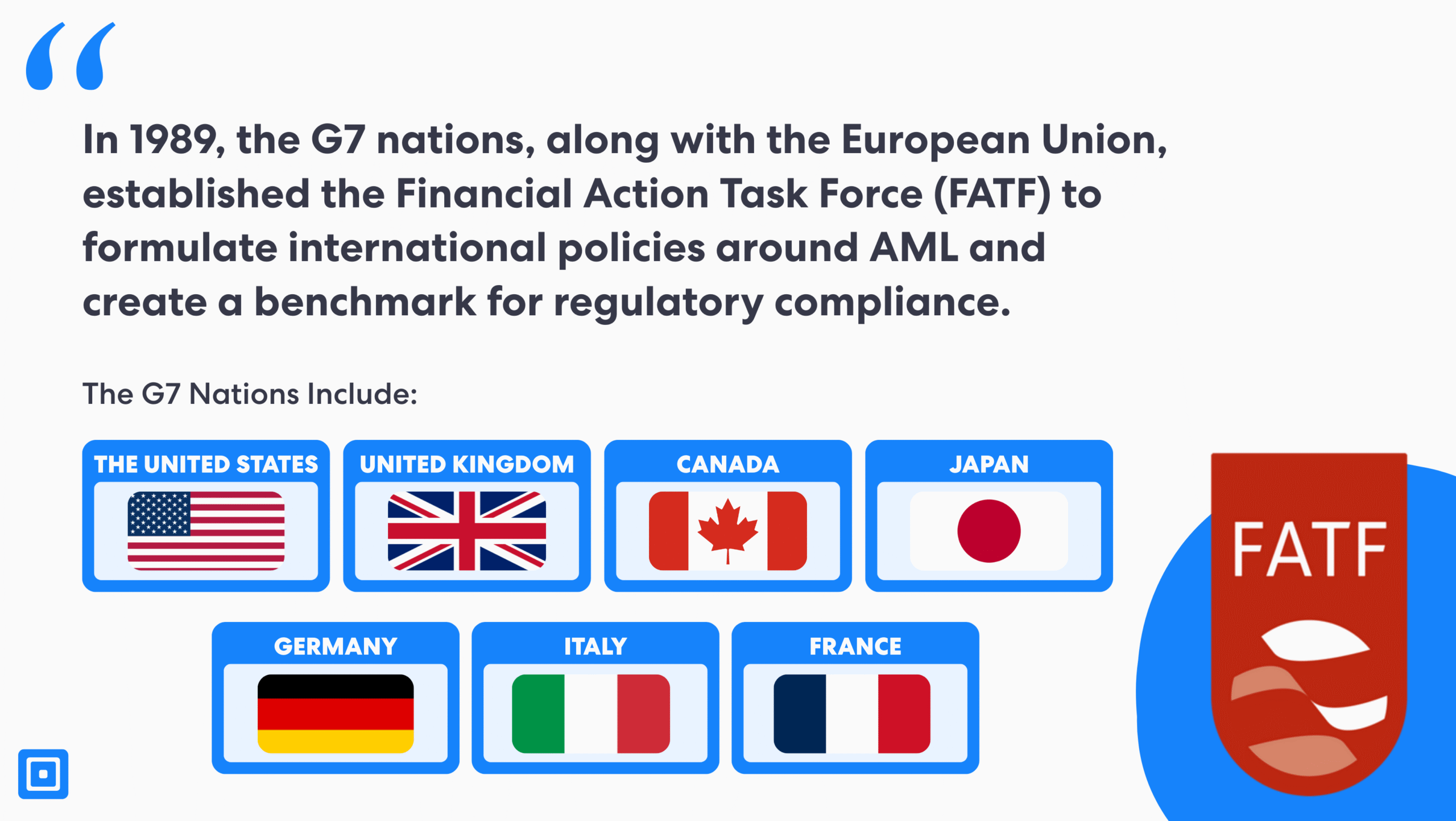
To stabilize the economy, countries worldwide decided to take a more united and collaborative approach to ensure compliance. For instance, in 1989, the G7 nations, including Canada, the United Kingdom, the United States, and the EU, established the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) to formulate international policies around AML and create a benchmark for regulatory compliance in financial sectors and beyond.
National and Regional Adoption
The FATF’s standards for customer identification, risk assessment, due diligence, and ongoing monitoring set the standard in over 200 jurisdictions. These global norms were internalized and implemented by states and regions worldwide until today.
- European Union: The current Sixth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (6AMLD) requires financial institutions and a wide range of non-financial businesses to implement robust Customer Due Diligence (CDD), verification of beneficial ownership, and maintain ongoing monitoring. These Know Your Customer (KYC) measures align and reinforce FATF standards.
- Latin America and Africa: Most countries on these continents have updated their legislation to evolve with FATF requirements. This came as a recognition of the value of secure and transparent financial systems. While aligning with global standards, these regions also tailor their approaches to reflect unique local policy needs for regulatory compliance.
- Asia: Countries including Singapore, Japan, China, and India possess stringent KYC requirements, generally governed by financial regulators or central banks. This approach are closely benchmarked against FATF recommendations. Some jurisdictions also adapt and enhance their KYC solutions to address local risks and evolving financial crime trends.
The widespread adoption of FATF standards demonstrates a unified global effort to adopt comprehensive KYC processes to proactively combat and assess associated risks of money laundering and terrorist financing act.
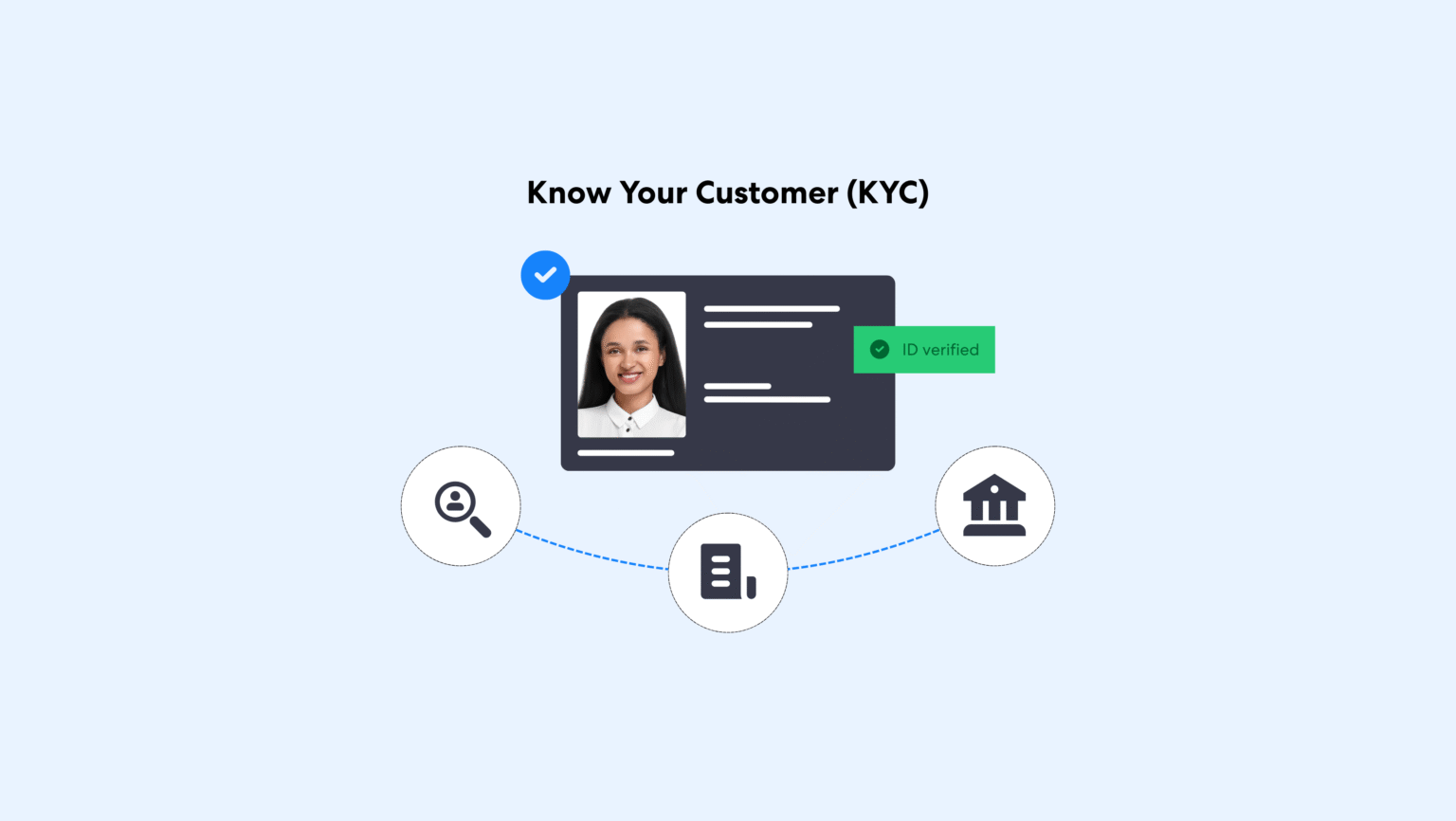
Demystifying the KYC Verification Process
The KYC process involves three core stages: the Customer Identification Program (CIP), Customer Due Diligence (CDD), and the Ongoing Monitoring stage. These stages have evolved over time in response to increasing money laundering risks and international regulatory standards. They also help businesses efficiently onboard corporate customers and merchants.
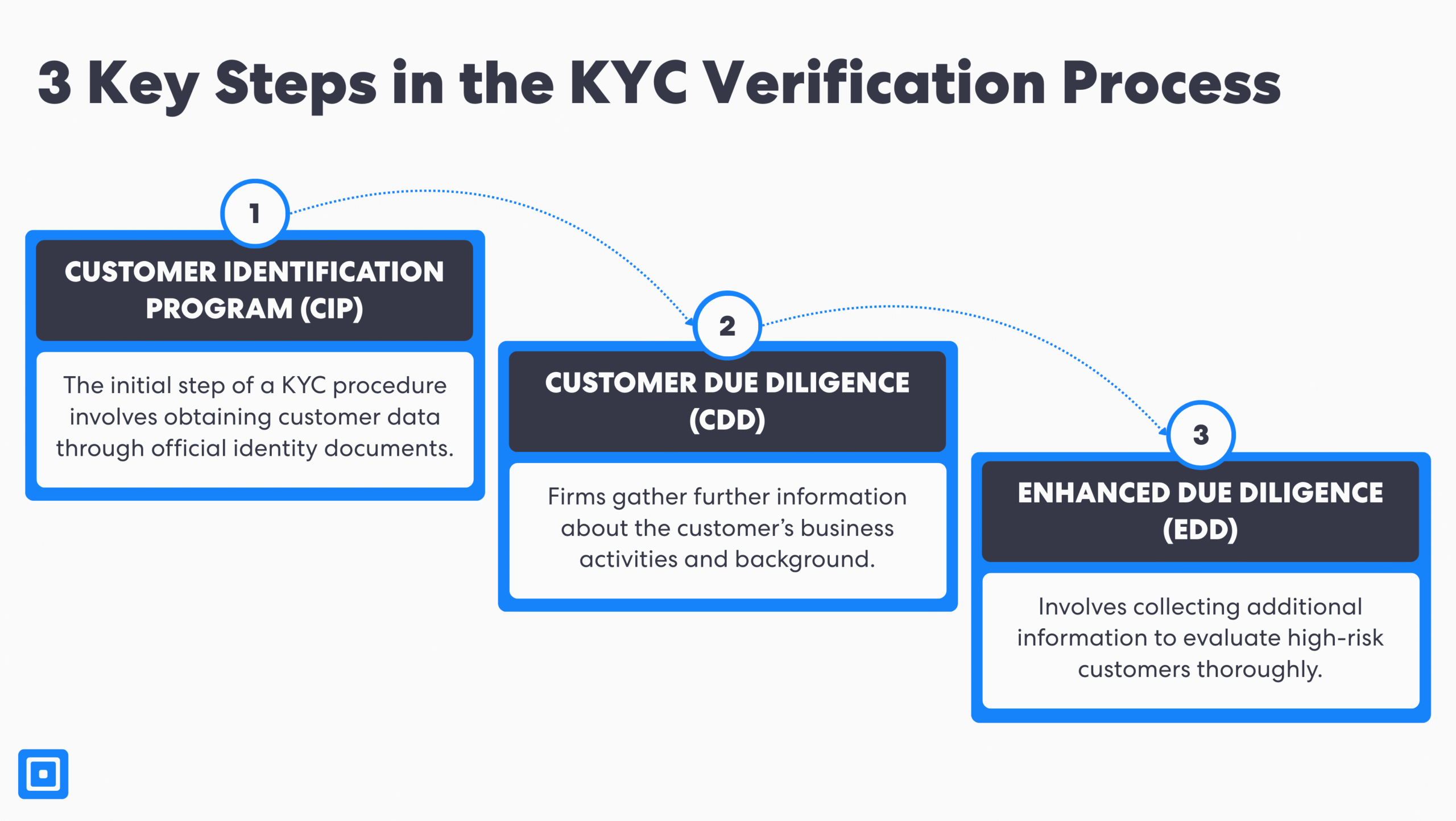
1. Customer Identification Program (CIP)
The initial step of a KYC procedure involves obtaining customer data through official identity documents such as passports or driver’s licenses. Important personal details, such as full name, date of birth, and home address, are gathered to help assess potential risk factors. This information enables compliance professionals to build a customer’s risk profile and identify associated risks in future transactions.
Verification methods to authenticate a customer’s identity include manual document checks or compliance software with advanced KYC and Anti-Money Laundering features. These features might include document verification, biometric checks like facial recognition, and other digital authentication methods. Using digital tools speeds up onboarding, improves customer experience, and strengthens the ability to detect suspicious activities early.
2. Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
The next stage is Customer Due Diligence (CDD), which forms a key part of the KYC onboarding process for financial institutions. Here, businesses gather more information about the customer’s business activities, financial background, and, where relevant, the intended use of their bank account.
This stage is crucial for Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance, enabling compliance professionals to effectively assess money laundering risks and assign an appropriate customer risk profile. The CDD process includes verifying the source of the customer’s funds, reviewing identity documents, and evaluating the nature of the customer’s transactions. For existing customers, ongoing monitoring ensures any behavior changes or suspicious activities are promptly reported to the relevant report analysis centre.
3. Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
Finally, there is the Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) stage. EDD goes beyond standard Identity Verification (IDV) and the initial KYC onboarding process. It requires gathering additional detailed information to assess risk and thoroughly evaluate high-risk customers.
This involves ongoing risk assessment through investigating business activities, extensive background checks, and transaction patterns. For example, financial institutions might ask for extra KYC documents and apply closer checks for high-risk customers, such as Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) or individuals on sanctions lists. These extra steps help prevent unauthorized people from accessing financial services or committing crimes like money laundering.
The Major Challenges of KYC Implementation
KYC verification prevents bad actors from committing crimes by verifying their identity and limiting their access at the beginning of the customer onboarding stage. However, while a robust KYC process is vital, a slow or confusing client onboarding process can harm the customer journey and cause frustration. For example, long delays and verification failures may cause a client to abandon onboarding entirely. Therefore, businesses must balance security with smooth onboarding to keep valid users while minimizing drop-offs.
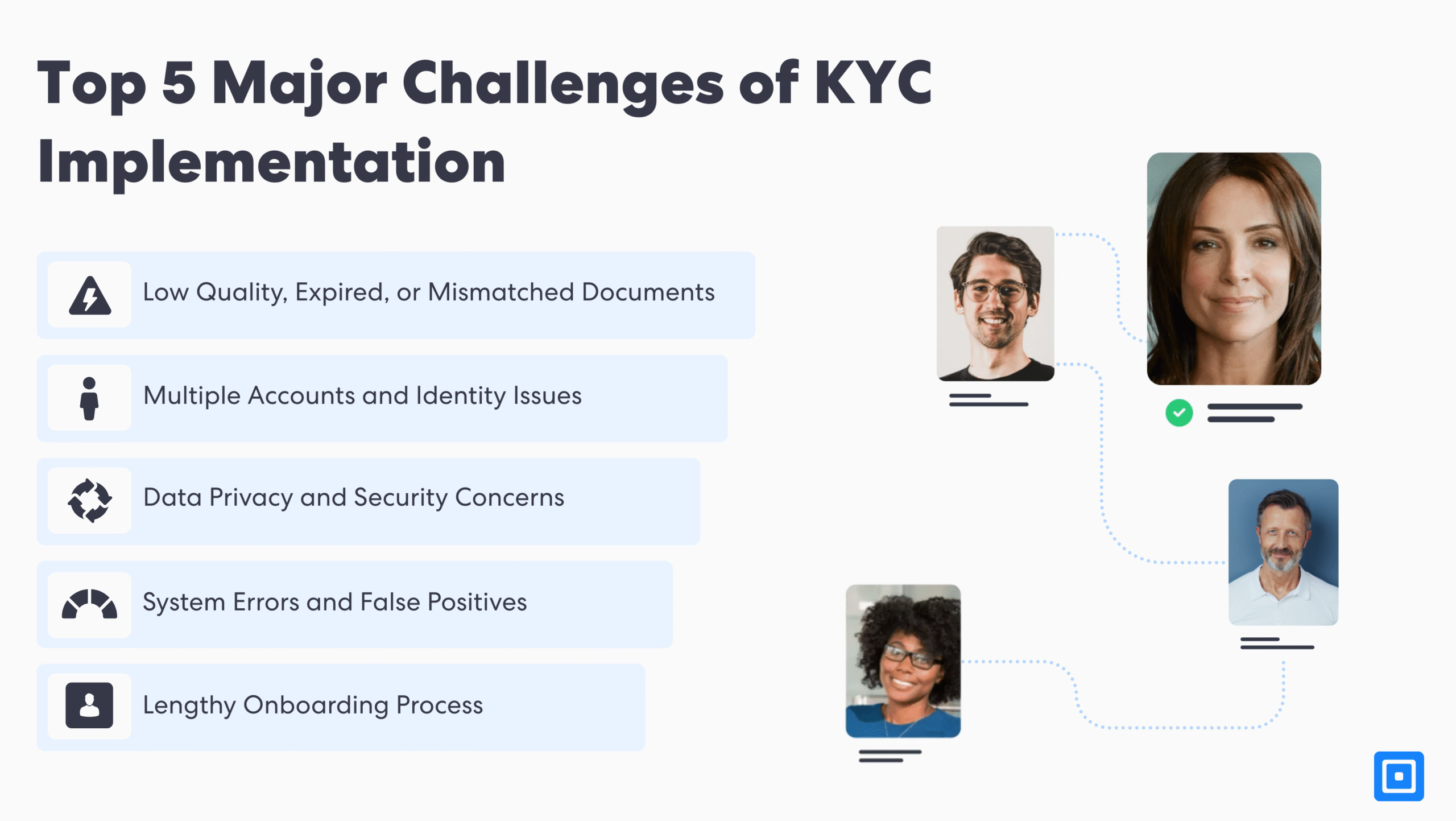
1. Low Quality, Expired, or Mismatched Documents
- Challenge: One common challenge is customers failing to submit the correct identification documents during the onboarding process. For instance, they may upload expired IDs or unclear photos. Some other instances include submitting the wrong document type, all of which trigger verification failures.
- Solution: To address these challenges, businesses need to notify users ahead of time and clearly and understandably about the document submission requirements. Offering step-by-step instructions with examples of valid documents can significantly reduce mistakes. Furthermore, real-time feedback involving lighting tips or blur warnings helps users correct issues immediately.
2. Multiple Accounts and Identity Issues
- Challenge: Another common challenge is customers creating multiple accounts or deleting and recreating new accounts during verification. This can cause system alerts to flag or outright customer rejection. Sometimes, customers might forget their login details and attempt to restart the onboarding process.
- Solution: Guiding users to customer support instead of allowing repeated failed attempts can be beneficial. Additionally, backend systems that detect duplicate identities early and provide users with clear updates on verification status are crucial. Businesses can avoid friction by allowing users to update personal information safely without redoing the Know Your Customer (KYC) onboarding process.
3. Lengthy Onboarding Process
- Challenge: Overly complicated forms with multiple verification steps and unclear instructions often frustrate clients and cause many to abandon the process. Excessive friction during customer onboarding lowers conversion rates and can push actual customers away.
- Solution: Instead of a one-size-fits-all method, companies should use a risk-based KYC process to match checks to customers’ risk levels. For example, low-risk users can undergo simplified verification, while high-risk customers undergo deeper checks. Automated KYC and AI can accelerate document verification, reducing human intervention and delays.
4. System Errors and False Positives
- Challenge: False positives occur when genuine customers are classified as suspicious or fraudulent due to system errors, outdated databases, or overly restrictive algorithms. It causes client frustration and inconvenience, and can damage a business’s reputation.
- Solution: To prevent this, firms must leverage explainable AI models that are transparent, understandable, and free from hidden biases. Additionally, companies should vet and update these models regularly to detect new risks and minimize incorrect decisions.
Challenge 5: Data Privacy and Security Concerns
- Challenge: Customers often hesitate to give sensitive personal information due to data security and privacy concerns. Uncertainty about how personal data is used and processed will risk the loss of trust in the KYC onboarding process.
- Solution: Firms must explicitly state data protection policies and compliance with data protection laws. Additionally, using secure encryption for data storage builds stronger client and customer confidence. Highlighting compliance and security badges highlights alignment with regulations and fosters trust.
Future Trends in KYC: Staying Ahead of the Curve
As technology and regulatory standards evolve, Know Your Customer (KYC) solutions are advancing to streamline the customer onboarding process and enhance the overall customer experience.
These improvements help financial institutions increase ROI by maintaining compliance with strict KYC requirements while delivering a smoother, more efficient onboarding process.
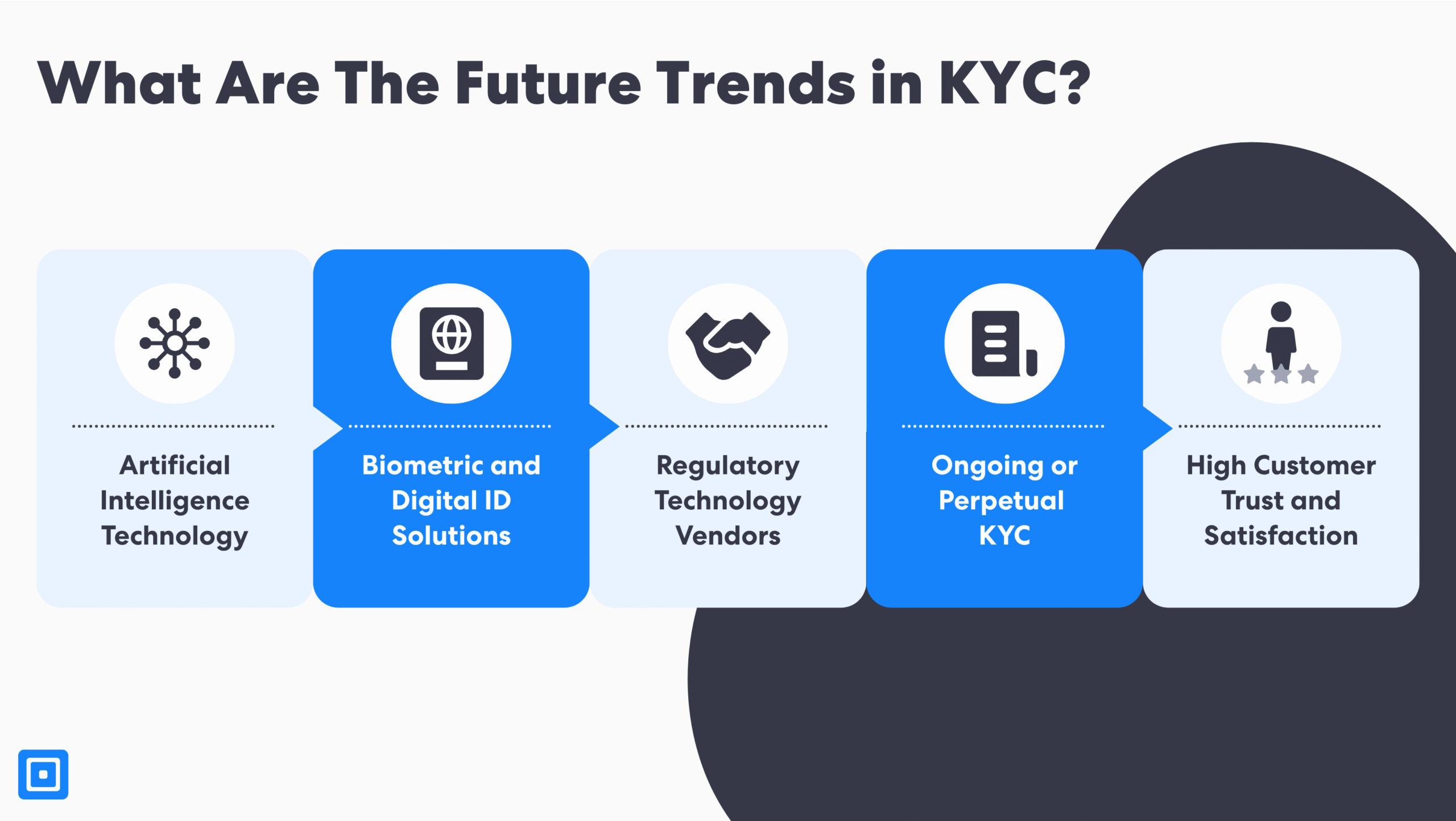
The Use of Artificial Intelligence Technology
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been reshaping KYC by streamlining identity verification, risk assessment, and transaction monitoring through automation. AI is able to scan bulk data, identify patterns and flag anomalies at a rapid pace while significantly increasing accuracy. This helps reduce false positives compared to manual KYC processes which are prone to human error and inconsistencies.
Biometric and Digital ID Solutions
Biometric authentication, including facial recognition, is increasingly used to verify a customer’s identity with high accuracy. Features such as liveness detection ensures that the person undergoing verification is physically present, effectively distinguishing real users from deepfakes. This significantly reduces the risk of fraud during customer onboarding and high-risk transactions.
All-in-one Regulatory Technology (RegTech) Vendors
RegTech providers support businesses in getting ahead of regulations by making compliance checks and policy adherence easier. For instance, ComplyCube uses advanced AI to deliver real-time risk analysis, automate transaction monitoring, and centralize compliance management. These solutions are also scale with business growth, enabling firms to manage compliance obligations while reducing cost.
Ongoing or Perpetual KYC
Manual compliance procedures in the past relied on periodic reviews on a quarterly or bi-annual basis. With ongoing KYC, also known perpetual KYC, organizations can leverage real-time data feeds and continous monitoring. As a result, risk profiles can be updated within seconds, creating a proactive approach to dynamic regulatory compliance.
Maintaining Customer Trust and Satisfaction
Building customer trust and satisfying customer expections is vital for business reputation and growth. This is why companies are now prioritize a smooth and transparent customer onboarding experience to create a positive first impression, boost retention and foster loyalty. To achieve this, businesses leverage A/B testing to refine user interfaces and workflows, while closely monitoring drop-off rates and customer feedback to identify and address pain points in the onboarding journey.
By continuously refining the process based on real user data and Customer Satisfaction Scores (CSAT), businesses can enhance satisfaction and ensure that customers feel supported from the very beginning while maintaining significant ROI.
Build Trust at Scale with Robust Know Your Customer Process
Establishing a comprehensive KYC onboarding process is crucial for financial institutions to ensure compliance with money laundering regulations and protect financial transactions. By leveraging automated KYC for identity verification, businesses can continuously monitor customer transactions while streamlining onboarding, enhancing customer experience, and maintaining strict KYC compliance. Get involved today.